What is Spatial Computing?

Spatial computing refers to a set of technologies that enable human interaction with computers to happen in three-dimensional spaces. Instead of confining digital content and interactions to flat 2D screens, spatial computing integrates the physical and digital worlds.
Technologies under this term include virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality. Industry leaders believe that spatial computing will be the primary technological medium for human-computer interaction in the post smartphone era.

Understanding Spatial Computing
Multiple terms can be used interchangeably with ‘spatial computing’. These are:

Under these umbrella terms, key technologies include:
- Virtual Reality (VR): A computer-generated simulation that immerses users in a three-dimensional environment. Users can interact with the virtual space using specialized hardware, often in the form of headsets and controllers.

- Augmented Reality (AR): A technology that blends digital elements, such as graphics and sound, into the physical environment. Instead of replacing our surroundings like virtual reality, augmented reality enhances and enriches them, allowing users to experience a merged reality where physical and digital elements interact in real-time.

What is Mixed Reality?
Mixed reality is often described as a spectrum that indicates the level of digital immersion. On one end, we have the physical world, and on the other, fully digital worlds. This spectrum serves as a continuum for categorizing spatial computing applications based on their immersion into the digital realm.
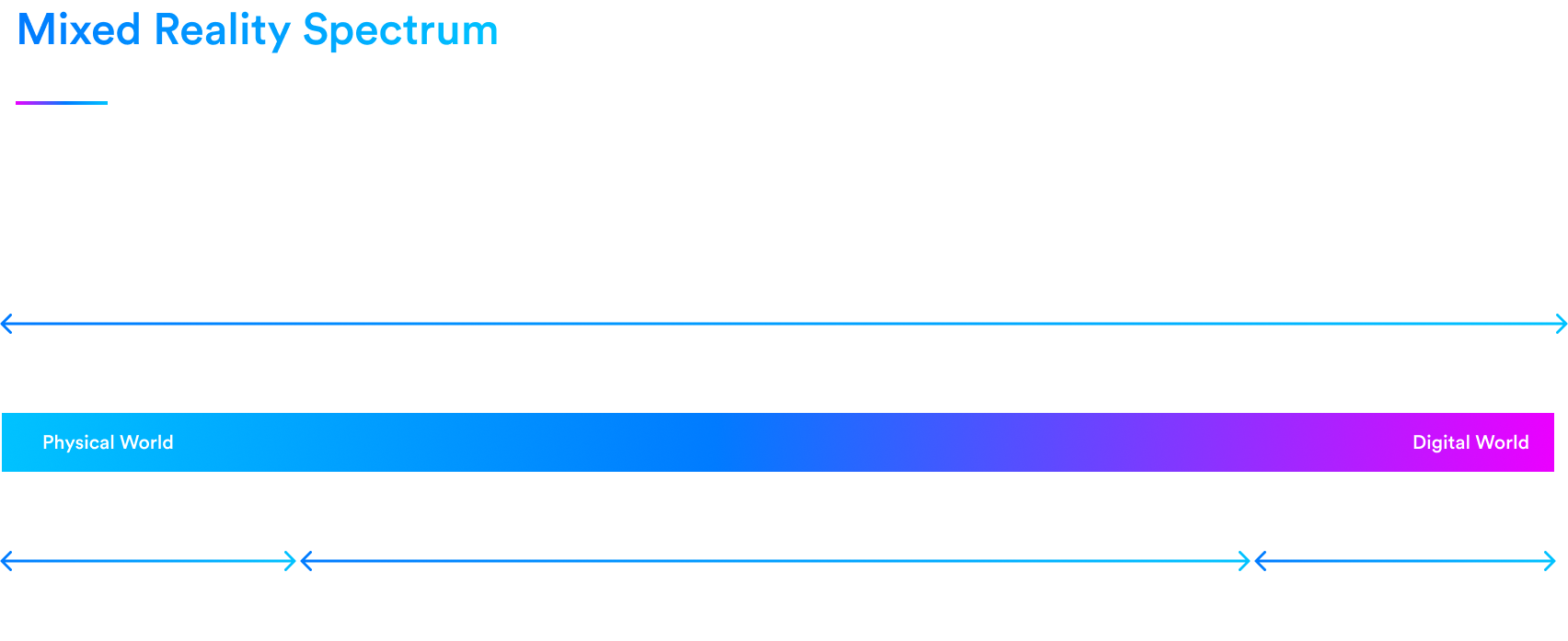
It is important to note that while both mixed reality and spatial computing relate to technologies that overlay digital information onto the physical world, they are not synonymous terms. Spatial computing encompasses a broader range of experiences, including virtual reality. Though VR is a form of spatial computing — offering fully immersive digital environments — it does not involve the physical world, and therefore is a different concept from mixed reality.
The Next Computing Platform
Many experts and technology leaders anticipate that spatial computing will be the next computing platform, succeeding the smartphone generation. This vision foresees a transformation in our relationship with technology, elevating human-computer interactions to unprecedented heights and ushering in a new technological paradigm.
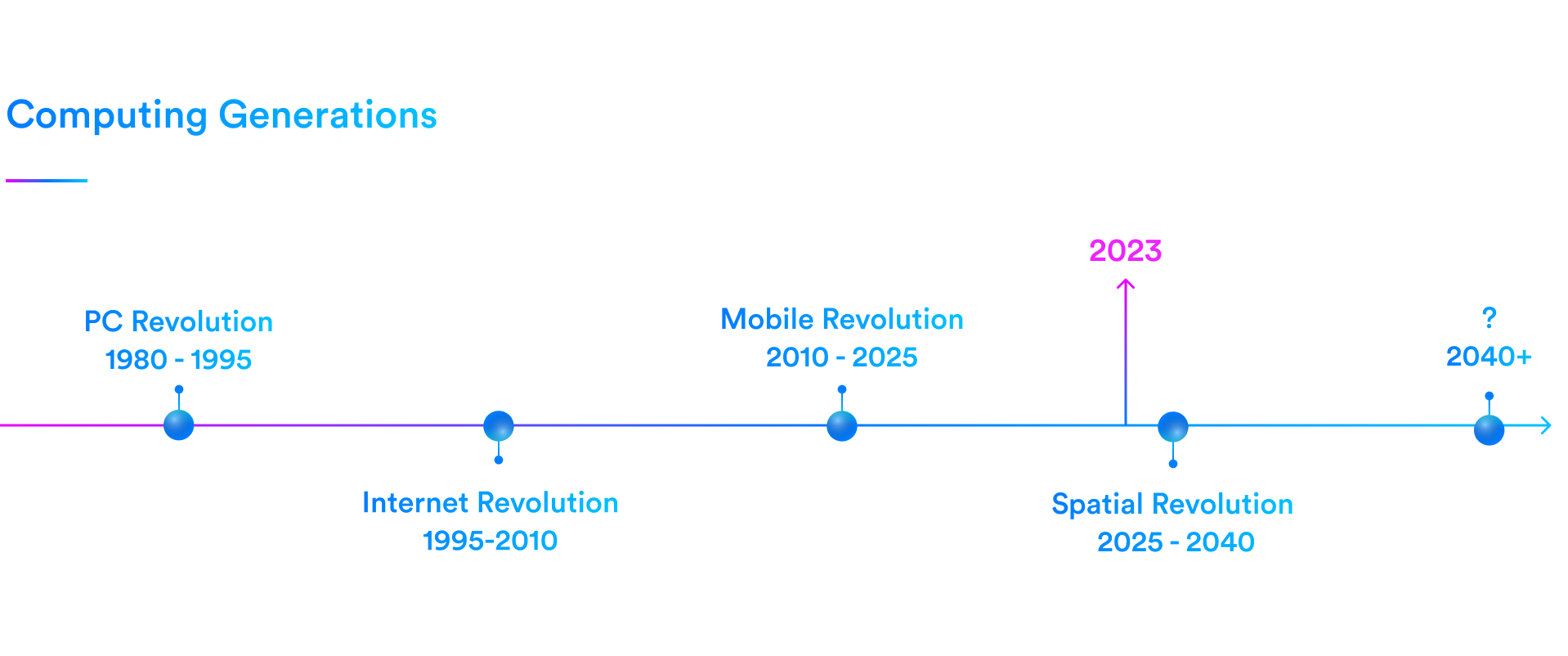
Over the past half-century of human progress, we've observed a consistent pattern driven by computing eras. Each generation has introduced a new technological paradigm that has transformed the way humans interact with technology.
Until now, technology has always been encapsulated in a box and viewed through a screen. Spatial computing will tear down the divide between the physical and digital worlds, creating a seamless blend between reality and technology.
“History never repeats itself, but it does often rhyme.” - Mark Twain

Examples of Spatial Computing Applications
Today, spatial computing is used across multiple industries and sectors. Here are a few examples of how this technology is being deployed today.
Training
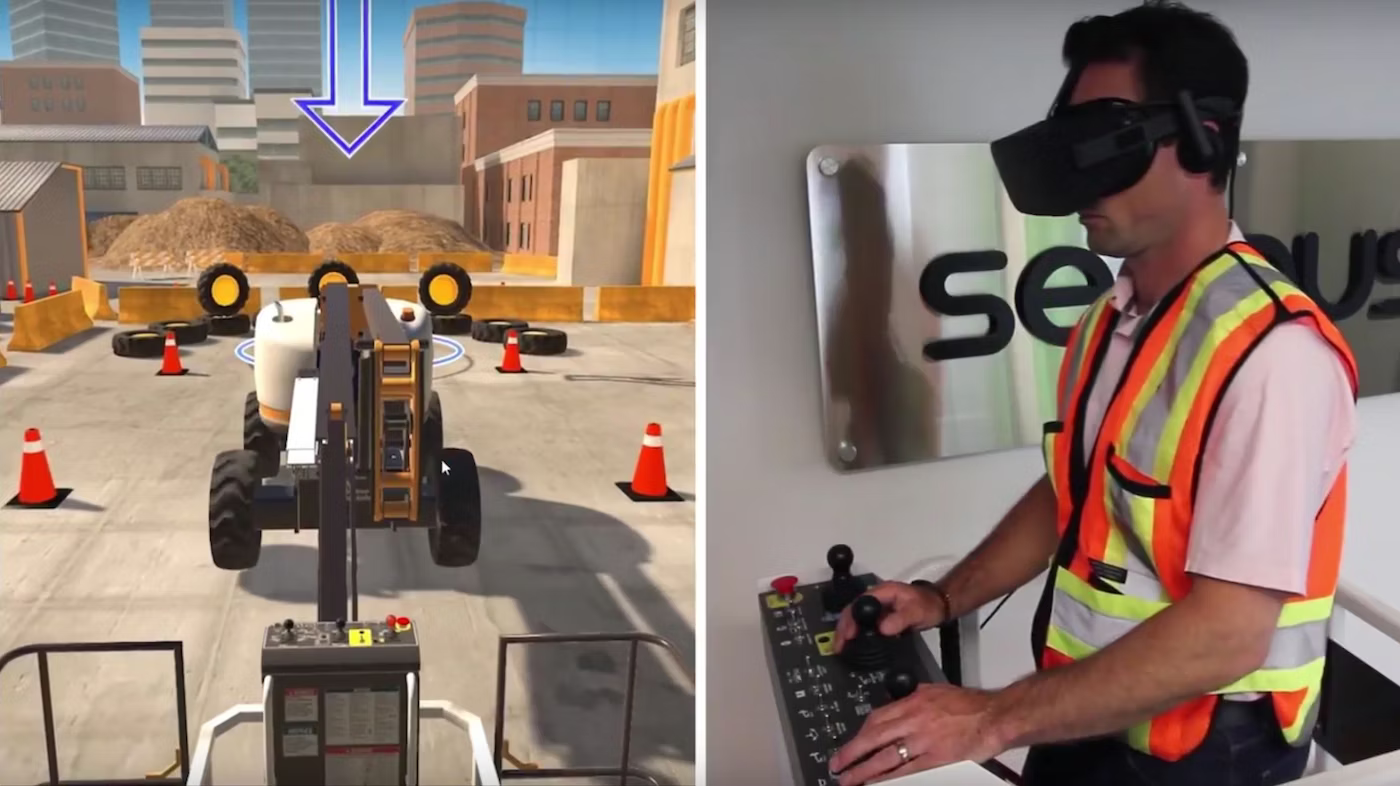

Spatial computing training simulators have had a huge impact on the enterprise and business sectors. Multiple industries and institutions have conducted studies comparing spatial training vs traditional training and seen phenomenal improvement in adopting these new technologies.
Spatial computing introduces a new paradigm to workforce training unlocking unique capabilities such as:
- Hands-on learning: multi sensory training enabling trainees to learn by doing.
- Safety: allowing for fail safe environments without real-world repercussions.
- Remote distribution: software that can be deployed remotely with off the shelf hardware enabling training scenarios like pre-hires or offshore job candidates.
- Scalability: software is developed once and then distributed with no marginal cost to as many trainees in the future. These simulations also require no physical infrastructure, resources or hands-on support from training staff.
For more examples of training see: Spatial Computing: A Complete Guide - Training
Remote Collaboration
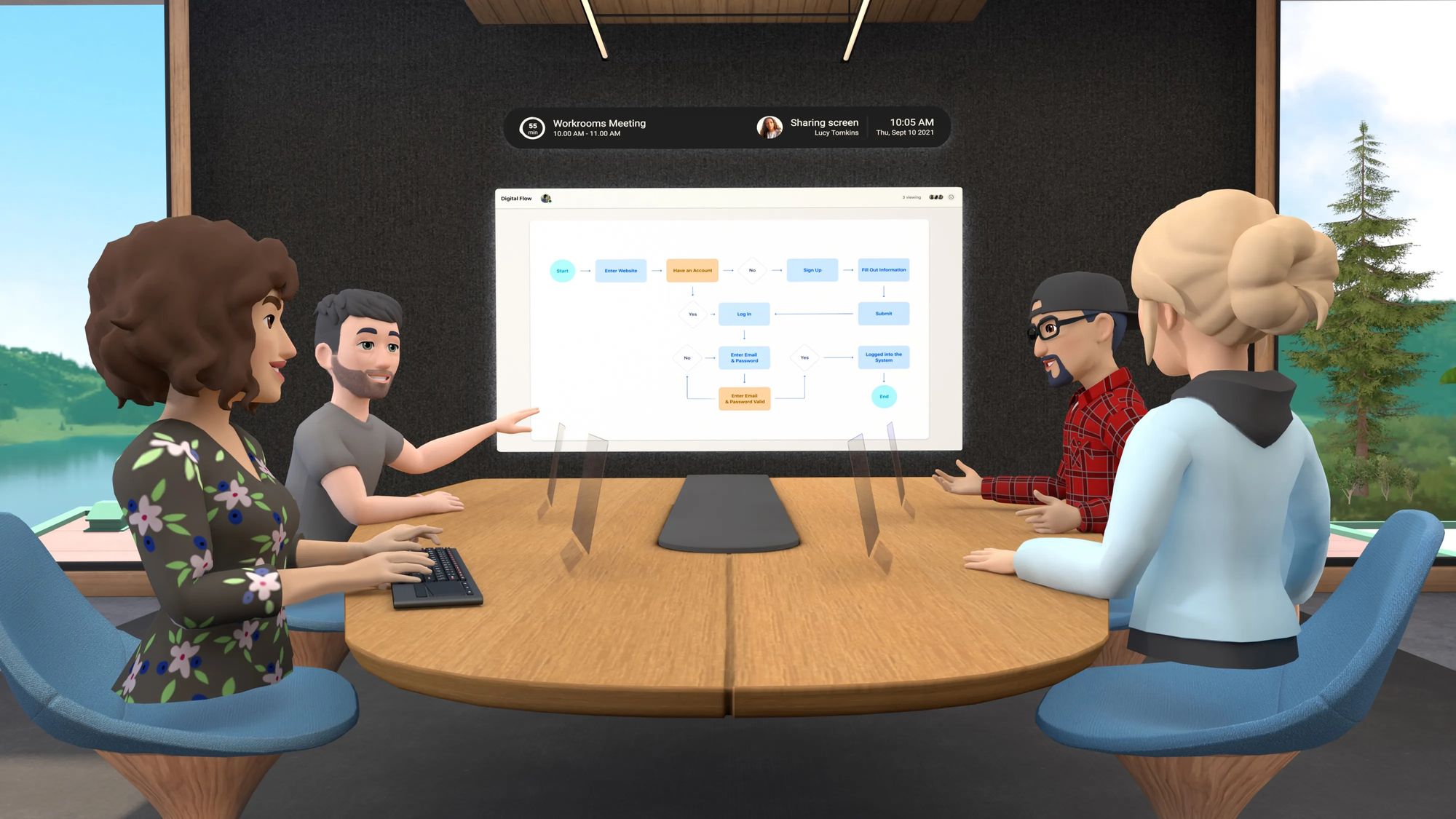

As more companies adopt remote or work-from-home formats, there has been an increase in the demand for more communication tools to bridge the gap in communication and collaboration that Zoom video meetings can't fully address.
Spatial computing allows teams to enhance presence in the digital workspace, leading to closer personal connections and a more immersive form of collaboration.
Many companies use spatial computing collaboration tools as an intermediary between Zoom and face-to-face meetings.
Manufacturing
Companies like Airbus and Toyota use spatial computing to refine their operational floor processes. By utilizing tools like Microsoft Hololens, engineers and designers can see and interact with holographic representations of manufacturing components, systems, and designs.
This enhances their understanding of manufacturing components, provides access to essential design information on-site, and equips workers to make informed decisions, resulting in increased accuracy and efficiency in manufacturing.
Such utilization of spatial computing leverages the technology to elevate both operational performance and the proficiency of their workforce, paving the way for future industry practices.
Education
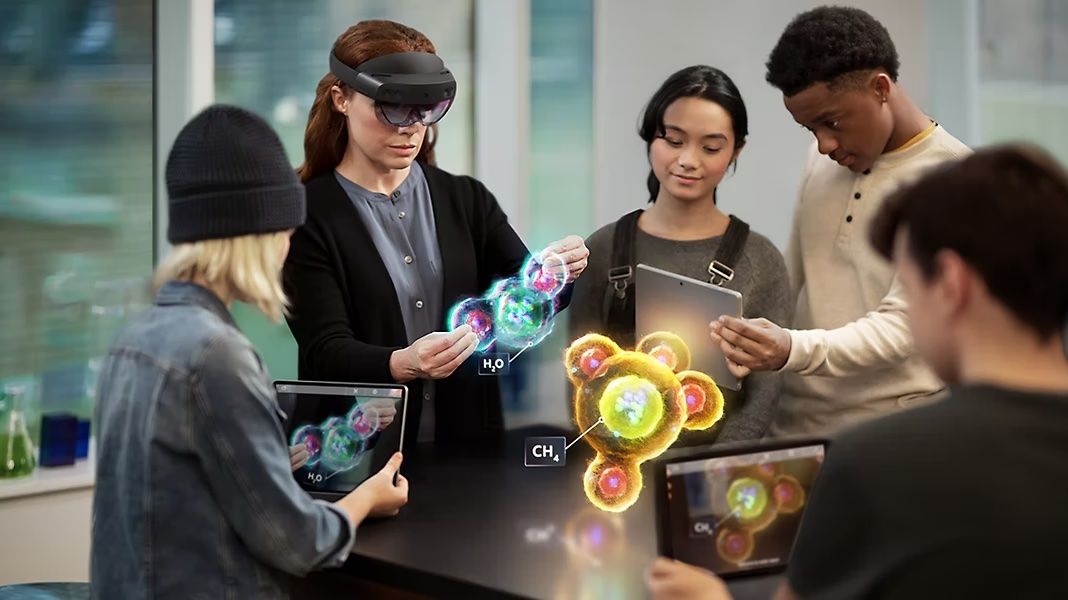

Education remains one of the sectors with the least innovation in society, as students are often still confined to the traditional classroom setting.
As experiential learning gains traction globally, we'll increasingly witness the embrace of new technologies like spatial computing that elevate experiential learning. This approach to learning, which stresses the importance of action and reflection, stands in sharp contrast to older, more passive teaching techniques.
Spatial computing enhances the educational experience by making it more engaging and immersive, underscoring the significance of social and emotional learning. Such technology equips students to explore, navigate, and comprehend complex concepts within a vibrant virtual environment.
For more examples on how spatial computing is being used today see: Spatial Computing: A Complete Guide - What is Spatial Computing Used For?

How Does Spatial Computing Work?
Spatial computing is a technology that allows users to blend the physical world with digital content using headsets. This is achieved through:
- Display technology that projects digital content onto a user's visual field of view. Virtual reality provides a fully immersive display experience, while augmented reality blends the physical environment with digital content.
- Sensors that detect the user's movements and environmental changes allowing for real-time adjustments to the digital overlay.
- User input through controllers, hand gestures and voice commands, users can interact with and manipulate the digital content.
- Graphical rendering capabilities that enable the existence of digital assets, animations, and visual effects, making the digital content appear both realistic and immersive.
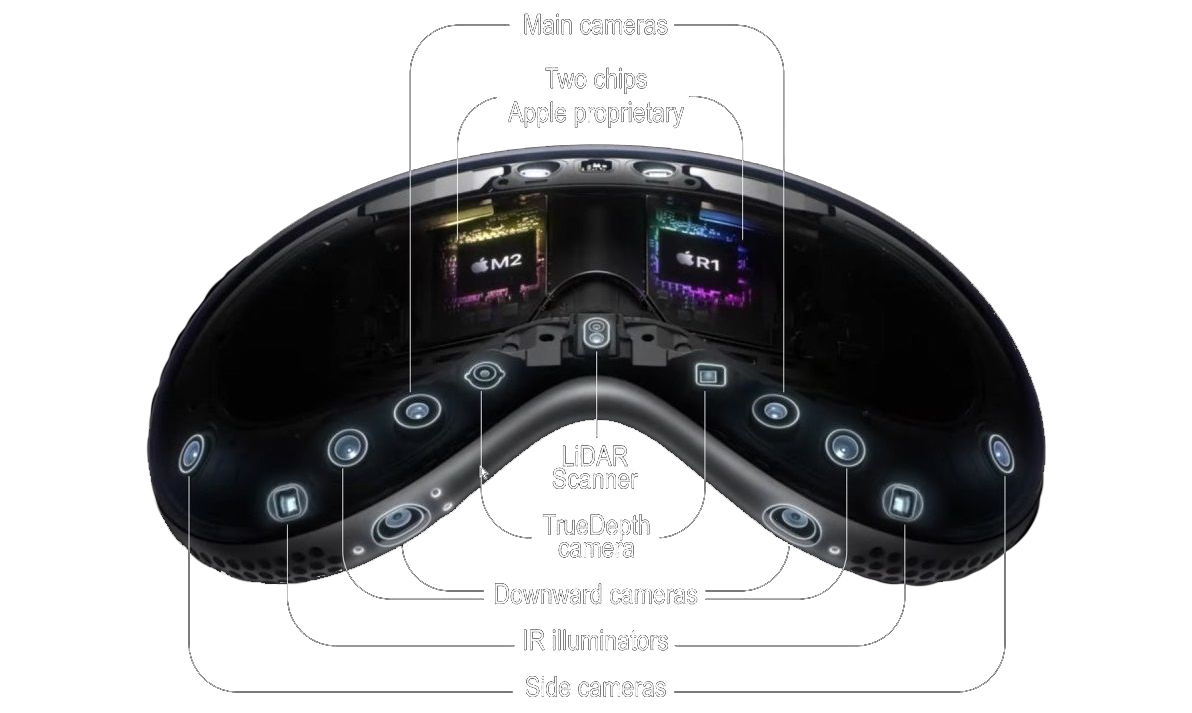
Spatial computing is made possible with the integration between these technologies, humans and the physical environments.

Companies Investing in Spatial Computing
Big Tech companies are strongly investing in spatial computing and competing to define who will become the leaders of this next computing platform.
Here are the list of the current industry leaders:
Apple
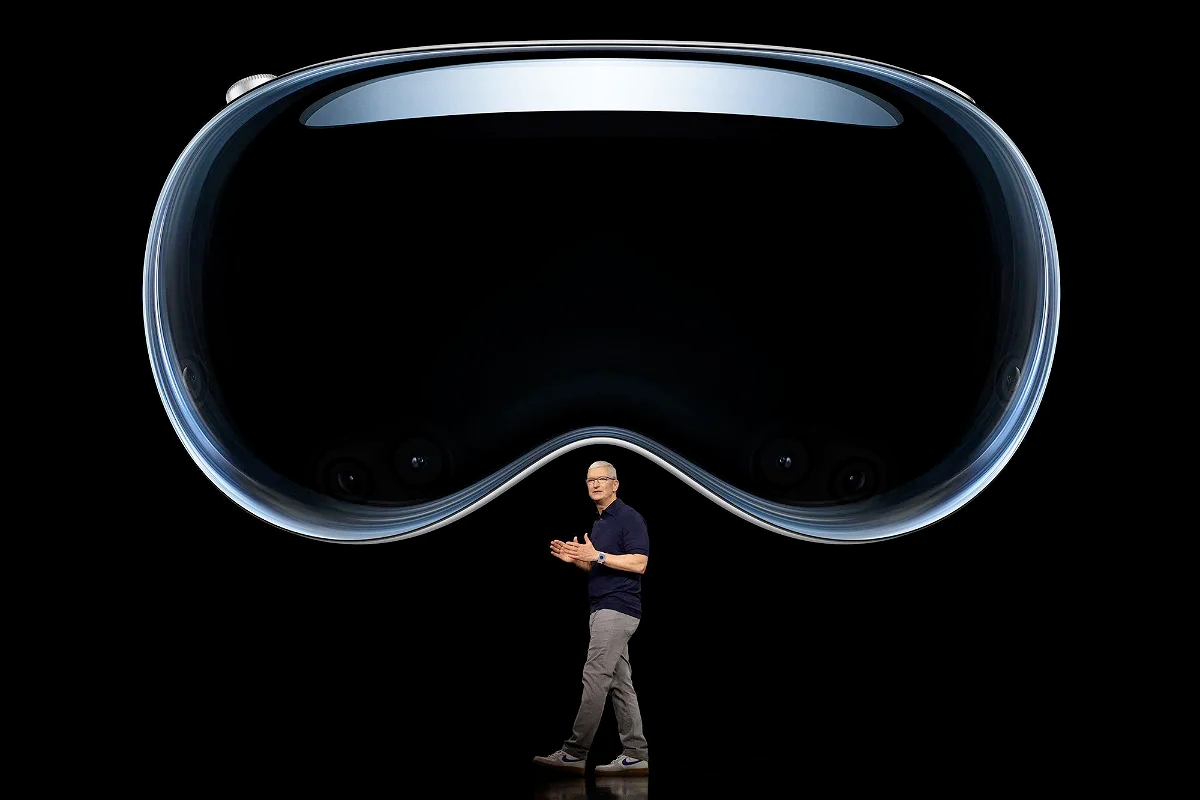

Apple has recently announced the Apple Vision Pro, the most advanced spatial computing headset on the market, featuring the most cutting-edge hardware available. This device is not targeted at the mass market; instead, it is positioned to be a product class leader, comparable to the iPhone or the Macintosh, but in the category of spatial computing.
“In the same way that the Mac introduced us to personal computing and the iPhone introduced us to mobile computing, Apple Vision Pro will introduce us to Spatial Computing. This marks the beginning of a journey that will bring a new dimension to powerful personal technology.” - Tim Cook, CEO Apple
Meta
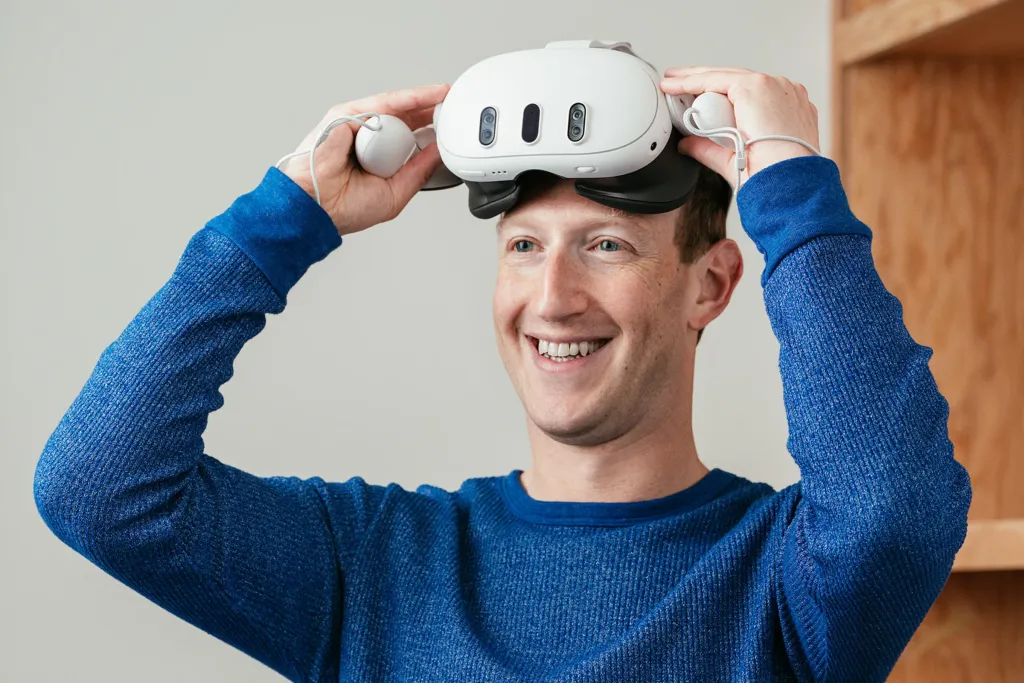

Meta is strategically positioned to benefit from the growth of spatial computing in the coming years. The new Meta Quest 3 is a fully integrated mixed reality headset, available at an affordable price of $499. While it offers functionalities that rival the Apple Vision Pro, it does so at a significantly reduced cost. This combination of affordability and performance positions the Meta Quest 3 as an attractive choice for a new generation of users exploring spatial computing for the first time.
“The basic story of technology in our lifetimes is how it's given us the power to express ourselves and experience the world with ever greater richness. We've gone from desktop to web to phones, from text to photos to video. But this is not the end of the line. The next platform and medium will be even more immersive, an embodied internet where you are in the experience, not just looking at it.” - Mark Zuckerburg, CEO at Meta
Magic Leap
Magic Leap, with their Magic Leap 2, is leading the space in enterprise. The company currently holds a portfolio of over 4,000 patents and leads the industry in glass display technology. While tech giants like Meta and Apple focus on the consumer market, Magic Leap has strategically positioned itself to cater to the growing enterprise sector, which is forecasted to experience considerable growth in the coming years.
Byte Dance
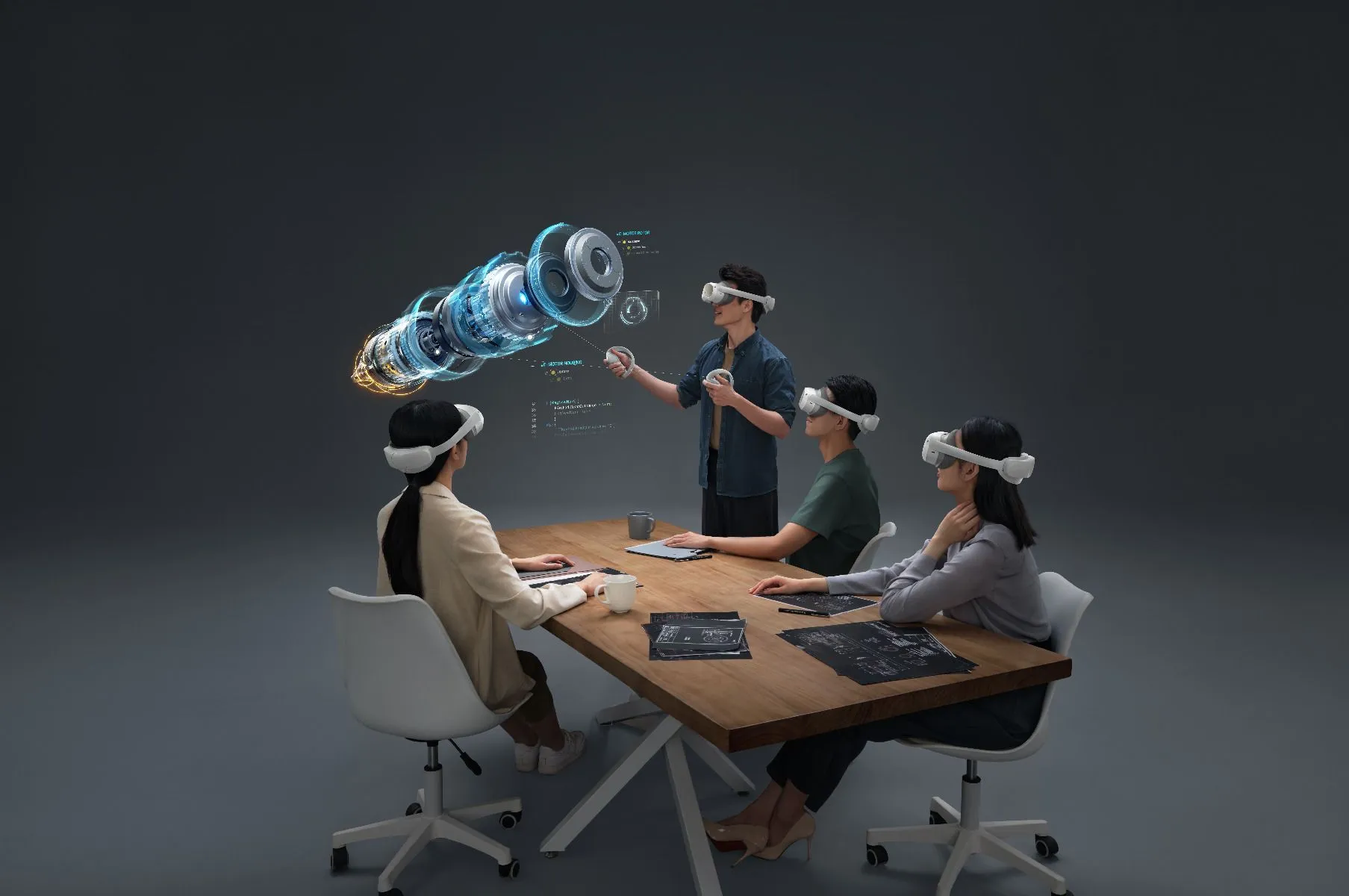

In 2021, the company behind TikTok, ByteDance, acquired the leading Chinese VR manufacturer, PICO. The company has recently launched the PICO 4, which directly competes with Meta’s Quest series. PICO also has a strong presence in the enterprise market with the PICO 4 Enterprise.
ByteDance is one of the world's largest tech companies, and with PICO, they are becoming a strong player in the spatial computing industry, leading in the Chinese market and holding a strong position globally.

The Future of Spatial Computing
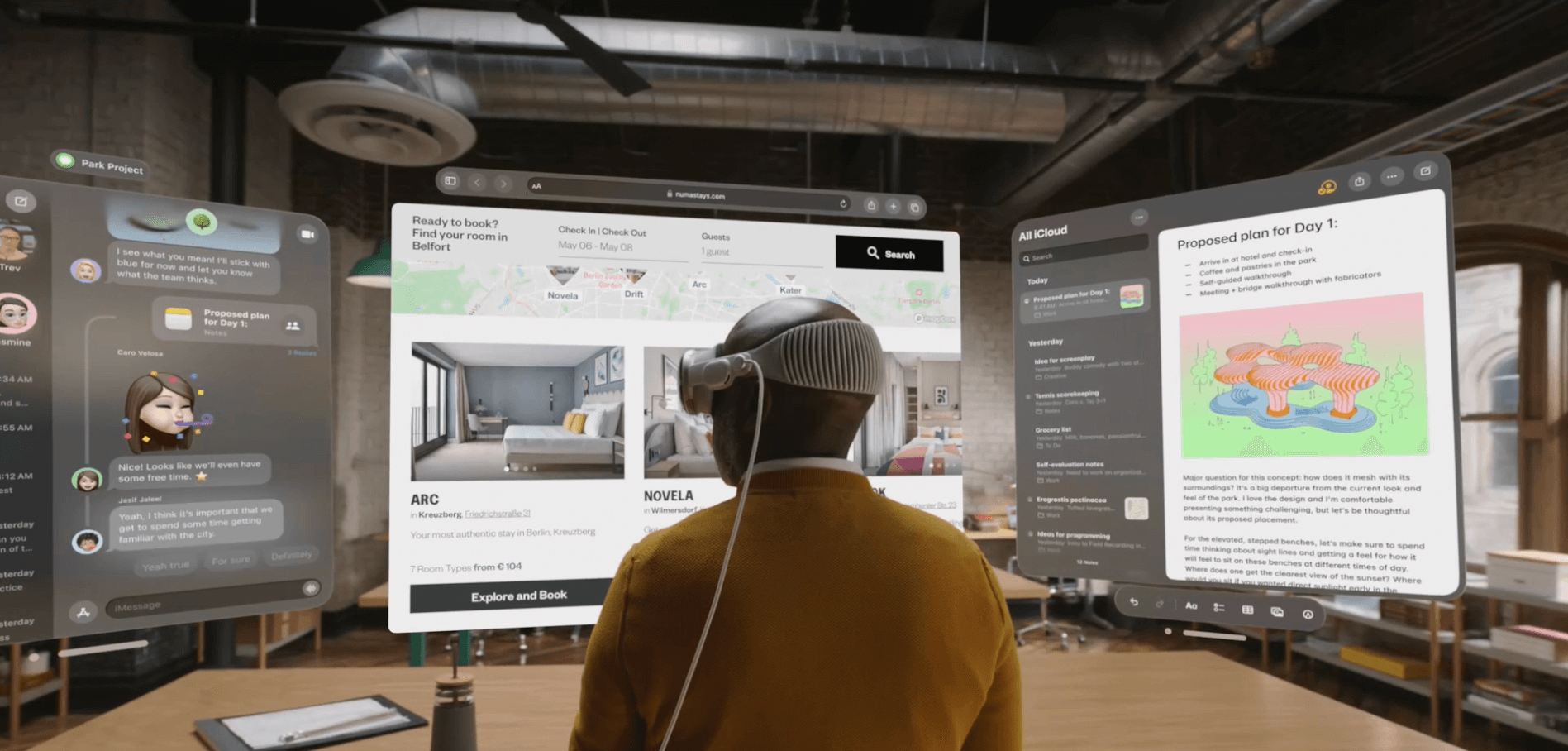
As we reach the end of the mobile-dominated computing generation, humanity will gradually transition to the next computing platform: spatial computing. We will move towards new ways of interacting with our everyday applications and witness a new wave of spatial applications and use-cases.
Apple's entry into the industry with the Apple Vision Pro, along with Meta's next-generation headset, is set to unleash a new wave of entrepreneurs eager to improve our lives and disrupt industries through innovation and new technology.
Ever since smartphones became popular, we've spent much of our time looking down. With spatial computing, we'll start looking up again and engaging with the world and technology in new ways.

Wrapping up
We hope this blog post helped synthesize and explain what is spatial computing, how it works, and the current state of the industry today.
The business opportunities in this new computing platform are immense. If you are part of a startup or corporation looking for a senior AR/VR development team, we can assist. Treeview is a high-end boutique AR/VR development studio specialized in B2B software applications. Contact us, and we can discuss the project details.
The future is now.
Until next time.




