The best mixed reality headset for most enterprises in 2026 is the Meta Quest 3, offering the optimal balance of MR capability, cost, and deployment scalability at $499. For organizations requiring premium visual fidelity, Apple Vision Pro remains the high-end benchmark.
Budget-conscious fleet deployments should consider the Meta Quest 3S at $299, while simulation-critical applications demand the high fidelity virtual reality visuals should consider Varjo XR-4. For safety-critical environments requiring optical transparency, such as surgical or industrial settings, the Magic Leap 2 is the best choice.

No universal "best" exists, only the best headset for a specific use case. Hardware-use-case mismatch, not hardware limitations, causes most MR implementation failures.
This guide provides an enterprise-focused ranking of the most relevant mixed reality headsets available in 2026, helping CTOs, Innovation Directors, and technology leaders match hardware capabilities to organizational needs.
TL;DR
What this guide covers: Enterprise-grade mixed reality headsets ranked by business utility, total cost of ownership, and deployment scalability.
Current best options: Meta Quest 3 (best overall balance), Apple Vision Pro (highest fidelity), Samsung Galaxy XR (AI-first workflows), Magic Leap 2 and HoloLens 2 (optical see-through AR), Xreal Air 2 Ultra (lightweight AR development), Varjo XR-4 (simulation-grade).
Key challenges: Hardware-use-case mismatch remains the primary cause of MR implementation failures; no universal "best" headset exists.
Enterprise opportunity: Organizations report that XR-trained participants were 4x more focused than e-learners, and felt up to 275% more confident when applying new acquired skills. In terms of costs, at scale, VR/MR achieves a 52% cost-reduction compared to traditional classroom training.
Feel free to read along or jump to the section that sparks your interest:
What defines a High-Quality Mixed Reality Headset?
Five technical factors separate capable mixed reality hardware from inadequate solutions for enterprise deployment:
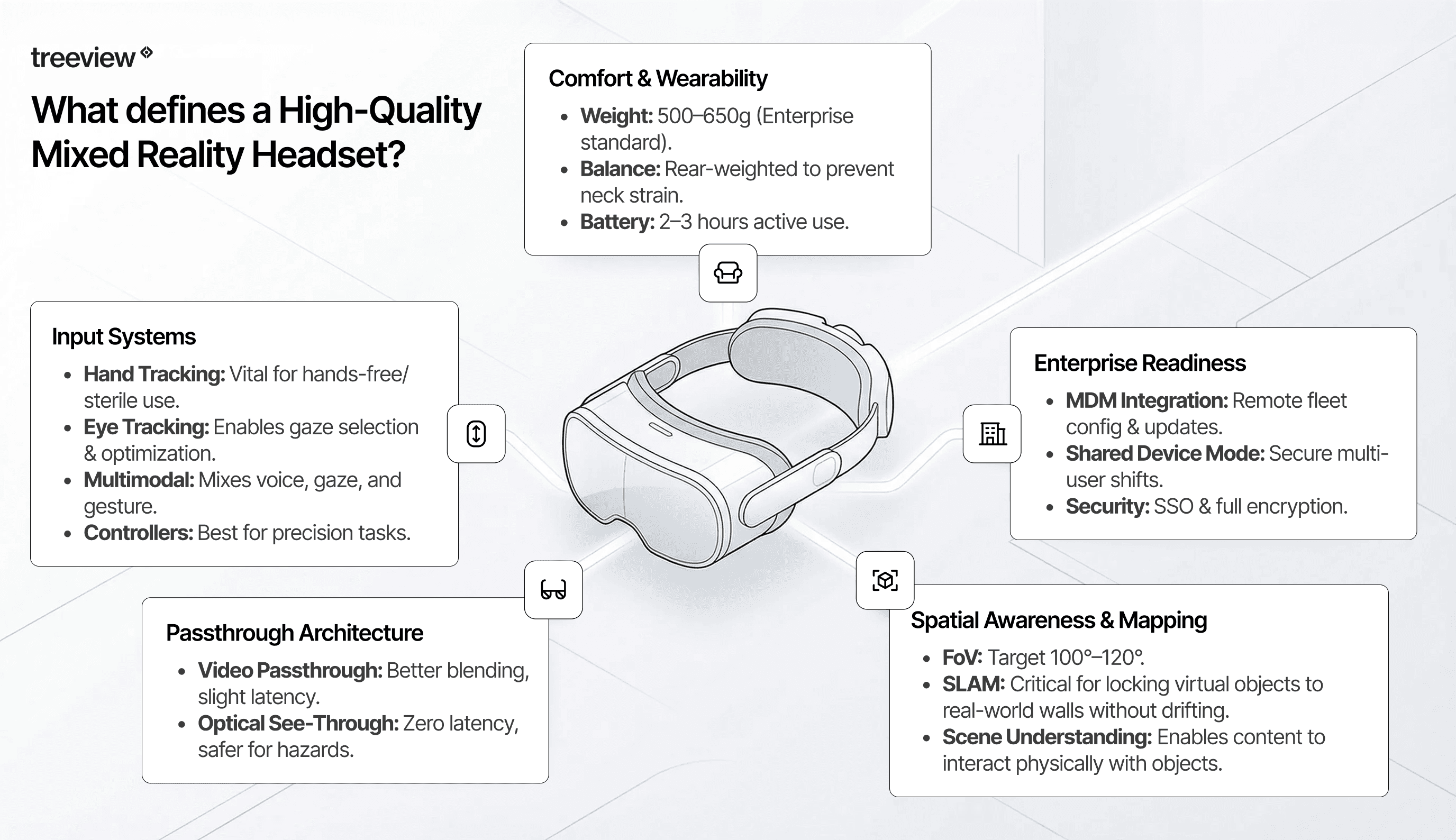
Spatial Awareness and Environment Mapping
The foundation of any mixed reality experience is how accurately the headset perceives and maps the physical environment.
Field of View (FOV): Determines peripheral awareness. Enterprise headsets typically range from 100 to 120 degrees horizontal coverage.
SLAM Quality: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping affects how reliably virtual objects maintain position relative to real-world surfaces.
Scene Understanding: Allows headsets to recognize furniture, walls, and obstacles, enabling virtual content to interact realistically with physical spaces.
Anchoring and Persistence: Determines whether virtual objects remember their placement across sessions.
Weak spatial mapping reduces true mixed reality to augmented reality overlays, undermining the value proposition for training and operational applications.
Passthrough Architecture: Optical vs Video
Modern mixed reality headsets employ two fundamentally different approaches to blending real and virtual environments.
Video Passthrough (Meta Quest, Apple Vision Pro, Samsung Galaxy XR) captures the real world through cameras and displays it alongside virtual content on internal screens. This approach enables superior virtual content integration but introduces slight latency between actual movement and displayed imagery.
Optical See-Through (legacy solutions like HoloLens 2 and modern iterations like Magic Leap 2) projects virtual content directly onto transparent lenses. While traditional versions limit brightness, newer devices employ dimming technology to mitigate this.
For enterprise deployment, video passthrough has become the dominant architecture due to its superior content integration and improving latency profiles.
Input Systems
User interaction methods significantly impact training effectiveness and operational utility:
Hand Tracking: Enables natural gesture-based interaction without physical controllers, critical for applications where workers need hands free or must maintain sterile environments.
Eye Tracking: Powers gaze-based interfaces and enables foveated rendering for performance optimization.
Voice and Multimodal Input: Supports hands-free operation essential for field service and medical applications.
Physical Controllers: Remain valuable for gaming-style training and applications requiring precise pointing or button inputs.
The best enterprise headsets support multiple input modalities, allowing mixed reality developers to choose the most appropriate interaction model for each use case.
Comfort, Battery, and Wearability
Weight distribution affects how long users can comfortably wear a headset. Front-heavy designs cause neck strain during extended sessions, while balanced designs using rear counterweights or external battery packs improve sustained comfort.
Factor | Typical Enterprise Range |
|---|---|
Weight | 500-650 grams |
Battery Life (standalone) | 2-3 hours active use |
Session Comfort | Varies by weight distribution |
Organizations planning extended training sessions or continuous operational use must factor battery management into their deployment strategy. Swappable battery designs and tethered power options provide workarounds for full-shift deployment.
Enterprise Readiness
Scalable enterprise deployment requires robust device management capabilities beyond consumer-grade features:
MDM Integration: Mobile Device Management enables IT teams to centrally configure, deploy, monitor, and update XR headset fleets at scale. Leading platforms like ManageXR and ArborXR are the industry standards for managing enterprise VR and MR deployments, providing remote provisioning, app distribution, policy enforcement, and device security across mixed hardware fleets.
Identity and Access Management: Determines how organizations authenticate users and control access to sensitive applications.
Shared-Device Modes: Allow multiple users to access the same headset with personalized settings, which is critical for training centers and facilities with rotating staff.
Security Posture: Encompasses data encryption, secure boot processes, and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
A mixed reality vendor can help you evaluate these factors early in project planning to avoid deployment complications.
Ranking: Top Mixed Reality Headsets (2026)
This ranking evaluates headsets based on enterprise value: the combination of MR capability, total cost of ownership, scalability, and ecosystem maturity. Consumer gaming appeal and technical specifications matter only insofar as they translate to business outcomes.
Headset | Price | Resolution (per-eye) | FOV | Weight | Battery | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Meta Quest 3 | $499 | 2064 × 2208 | 110° | 515g | ~2.2 hrs | Training, pilots |
Apple Vision Pro | $3,499 | 3660 x 3200 | ~100° | 800g | 2.5 hrs | Design, engineering |
Samsung Galaxy XR | $1,799 | 3552 × 3840 | 109° | 545g | 2-2.5 hrs | AI workflows |
Meta Quest 3S | $299 | 1832 × 1920 | ~96° | 514g | 2.5 hrs | Fleet deployment |
Magic Leap 2 | $3,499 | 1440 x 1760 | 70° | 260g | 3.5 hrs | Medical, Industrial |
Microsoft Holo Lens 2 | $3,500 | 1440 x 936 | 52° | 566g | 3 hrs | Microsoft ecosystem |
PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise | ~$800 | 2160 × 2160 | 105° | 580g | 3-4 hrs | Cost-sensitive |
Varjo XR-4 | $3,990+ | 3840 × 3744 | 120° | ~500g | Tethered | Simulation |
Xreal Air 2 Ultra | $699 | 1920 × 1080 | 52° | 83g | Phone-powered | Lightweight AR development |
#1 Meta Quest 3: Best Overall Balance
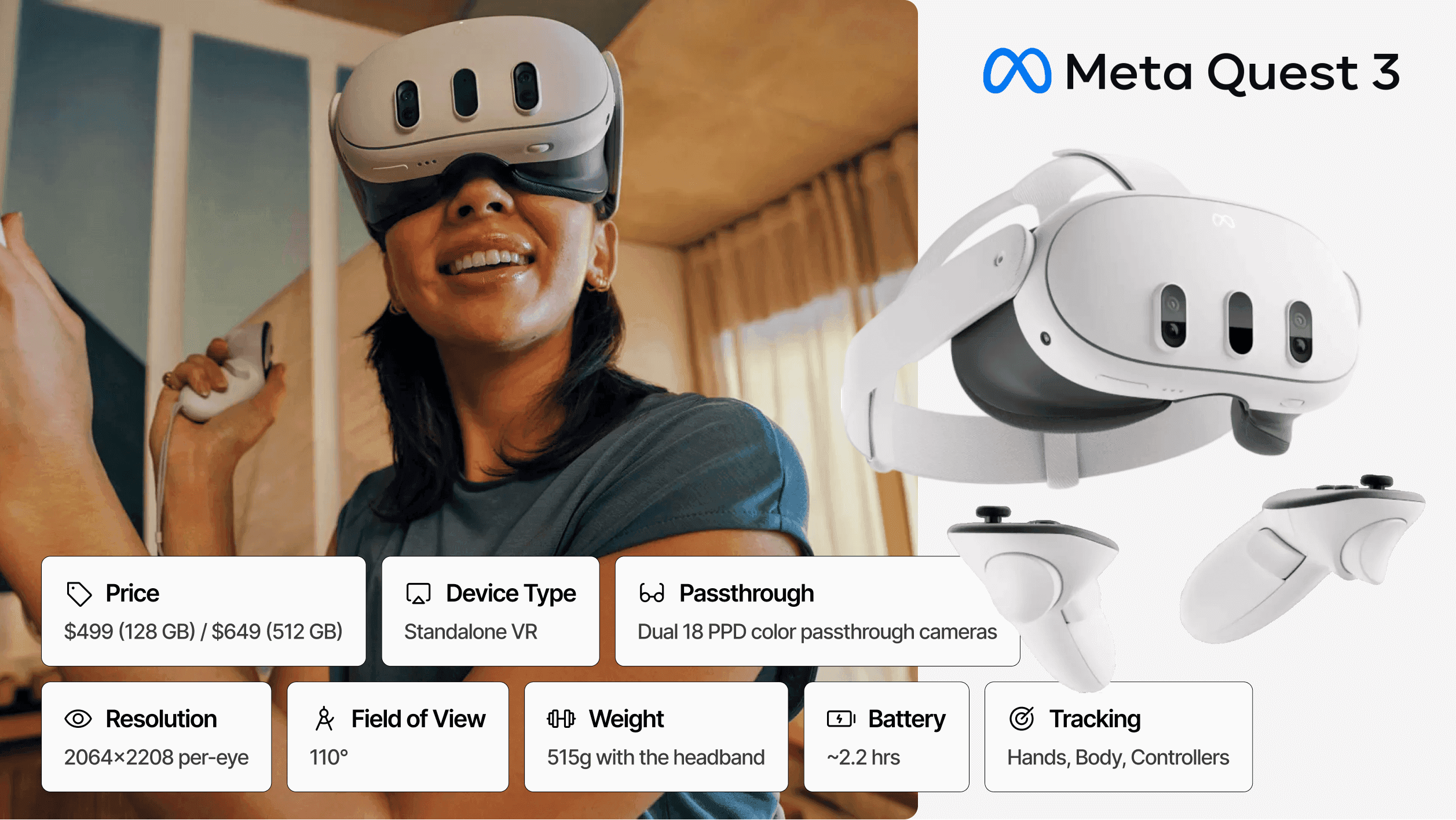
Price: $499 (128GB) | Architecture: Standalone | Passthrough: Video (color) | Resolution: 2064 × 2208 per-eye | FoV: 110° | Weight: 515g | Battery: ~2.2 hours
The Meta Quest 3 represents the optimal balance of MR capability, cost, and scalability for most enterprise applications.
Powered by the Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 processor with double the GPU performance of its predecessor, the Quest 3 delivers computational power necessary for complex training simulations and design visualization without requiring a tethered PC connection.
For enterprises seeking mixed reality developers or working with mixed reality agencies, the Quest 3 offers the largest ecosystem of development tools, third-party applications, and trained talent. Meta's mature device management infrastructure supports large-scale deployments, and the extensive application library provides immediate value while custom development proceeds.
Best For: Workforce training, enterprise pilots, scaled deployments, organizations beginning their MR journey.
Strengths:
Strong MR passthrough quality.
Excellent price-to-performance ratio.
Mature ecosystem and device management.
Large developer community.
Extensive application library.
Tradeoffs:
Passthrough fidelity below premium devices like Vision Pro.
Not safety-certified for hazardous environments.
No eye tracking.
#2 Apple Vision Pro: Best High-End Spatial Computing Workstation

Price: $3,499 | Architecture: Standalone (M5 chip) | Passthrough: Video (color, 12ms latency) | Resolution: 3660x3200 per-eye | FoV: ~100° | Weight: ~650g + battery | Battery: 2.5 hours
Apple Vision Pro sets the benchmark for visual fidelity in mixed reality.
The device features micro-OLED displays with 23 million total pixels and industry-leading 12-millisecond passthrough latency. The M5 chip upgrade in October 2025 delivered faster load times, sharper details, and up to 2× faster AI workloads compared to the original M2 model. For organizations requiring the highest visual precision, no current alternative matches Vision Pro's display quality.
Enterprise APIs support content protection, multi-user spatial collaboration, federated identity management, and device fleet integration. Deep Apple ecosystem integration benefits organizations already invested in Mac, iPad, and iPhone infrastructure, with features like Mac Virtual Display enabling seamless workflow extension.
Best For: Design reviews, engineering visualization, executive and knowledge-worker workflows, retail visualization, CAD collaboration.
Strengths:
Industry-leading visual fidelity.
Lowest passthrough latency (12ms).
Deep Apple ecosystem integration.
Optic ID biometric security.
Excellent eye and hand tracking.
Tradeoffs:
High cost limits fleet deployment.
External battery tether.
Limited ruggedization.
Shorter session battery life.
Weight can cause fatigue in extended sessions.
#3 Samsung Galaxy XR: Best Android / AI-First Alternative
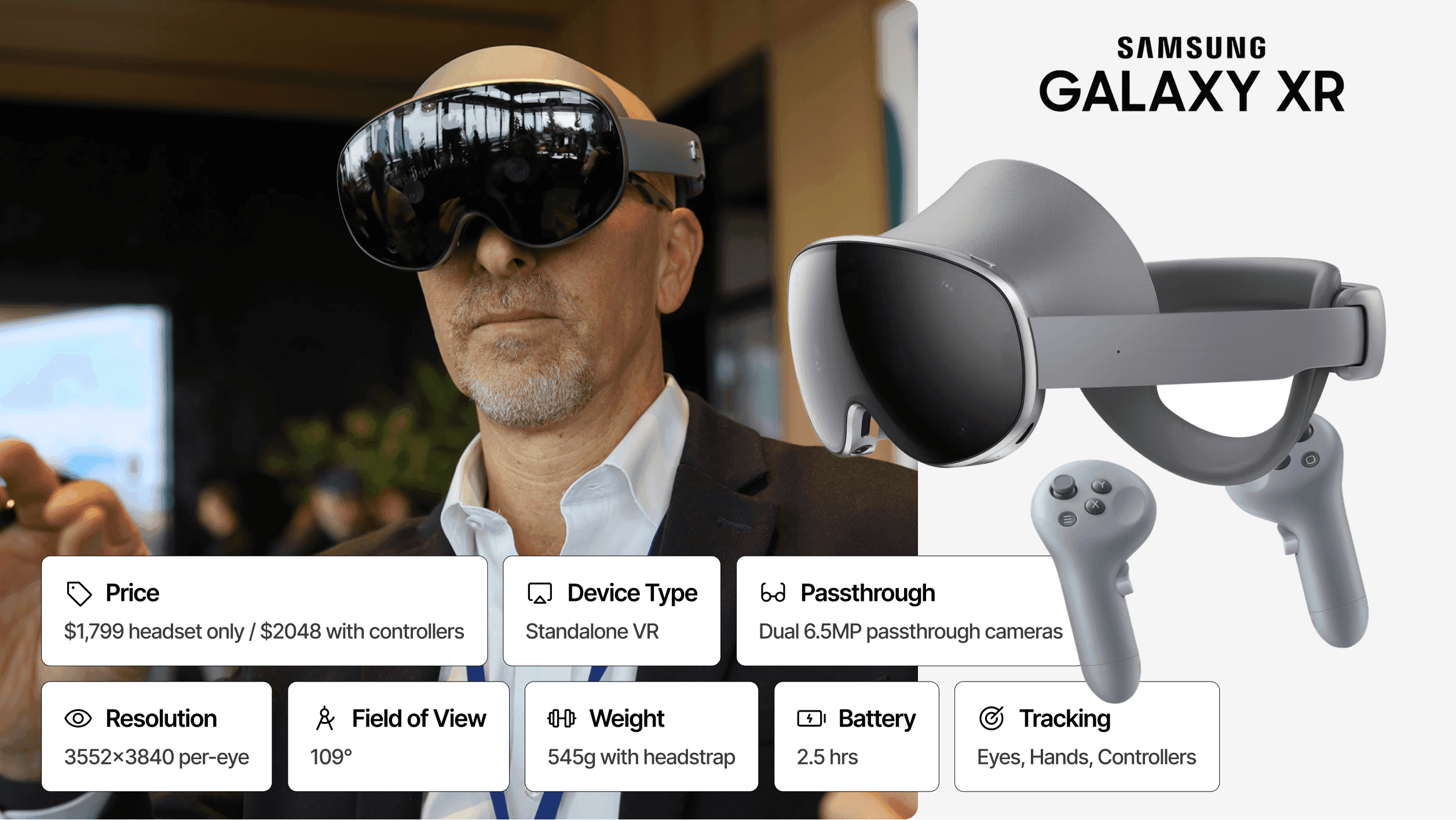
Price: $1,799 (controllers $250 extra) | Architecture: Standalone (Android XR) | Passthrough: Video (color) | Resolution: 3552 × 3840 per eye (27MP total) | FoV: 109° | Weight: 545g + external battery | Battery: ~2-2.5 hours
Samsung Galaxy XR represents the first major competitor built on Google's Android XR platform, offering a fundamentally different approach to mixed reality.
With Gemini AI deeply integrated throughout the experience, Galaxy XR enables conversational interactions about what you are seeing, contextual help within applications, and multimodal commands combining voice, gesture, and gaze. For enterprises already invested in the Android ecosystem, this platform alignment offers significant advantages.
Display specifications rival Apple Vision Pro, with dual micro-OLED panels delivering 27 million total pixels. Samsung Knox enterprise management provides robust security and device administration capabilities familiar to organizations already deploying Samsung mobile devices. Every existing Android app runs without modification, dramatically expanding available software from day one.
Best For: Android-native enterprises, AI-augmented MR workflows, organizations seeking Vision Pro alternatives at lower cost.
Strengths:
Gemini-powered multimodal AI.
Knox enterprise management.
Competitive display specifications.
Automatic IPD adjustment.
Android app compatibility.
Tradeoffs:
New ecosystem with limited real-world deployment history.
Controllers sold separately.
External battery tether.
Higher price than Quest 3.
#4 Meta Quest 3S: Best Budget MR Fleet Option
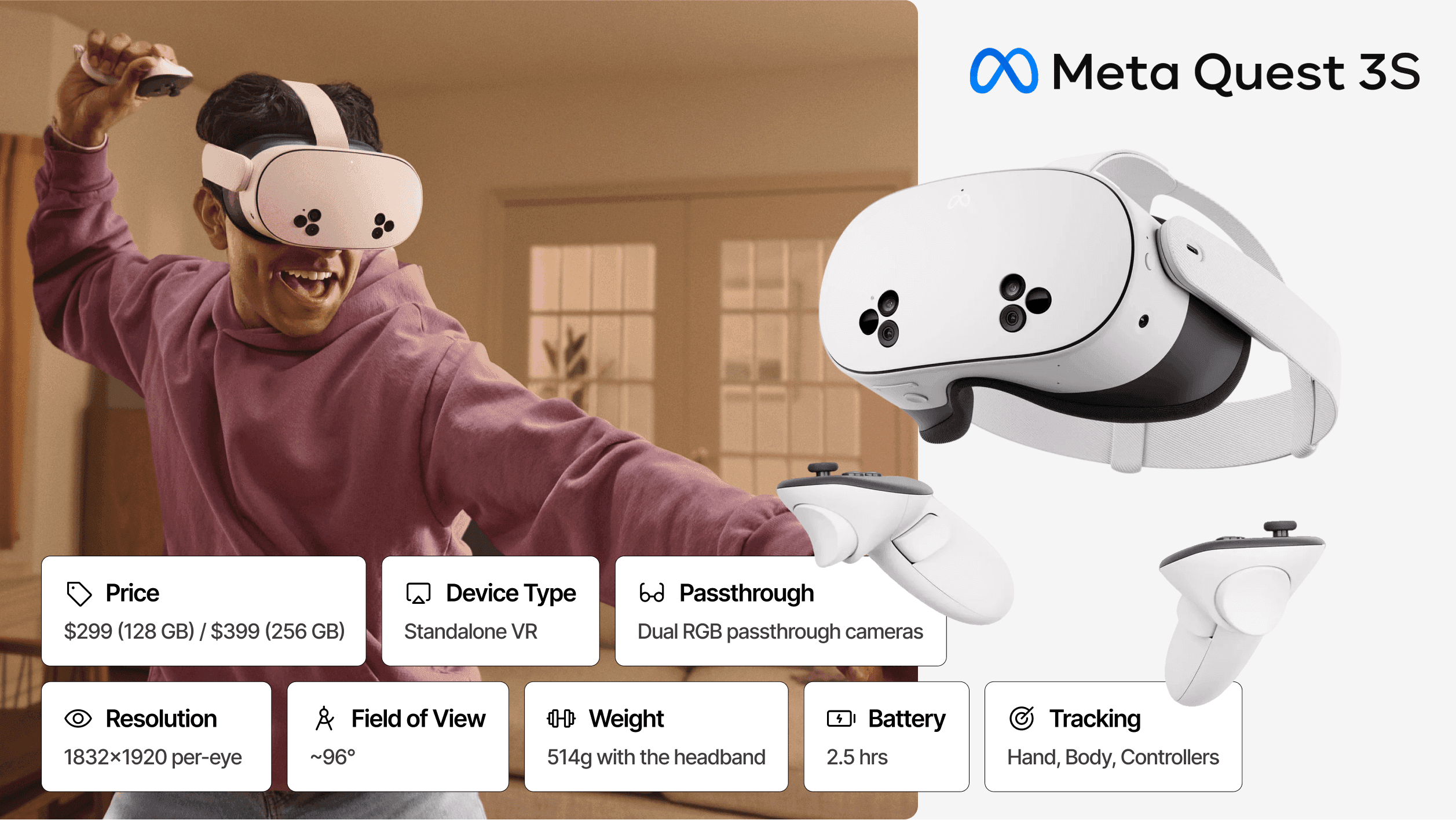
Price: $299 (128GB) / $399 (256GB) | Architecture: Standalone | Passthrough: Video (color) | Resolution: 1832 × 1920 per eye | FoV: ~96° | Weight: ~514g | Battery: ~2.5 hours
The Meta Quest 3S delivers entry-level mixed reality at unprecedented scale economics.
Despite its lower price point, it shares the same Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 processor and 8GB RAM as the Quest 3, meaning identical application compatibility and computational performance. The primary compromises come in display technology: Fresnel lenses instead of pancake optics create a smaller clarity sweet spot, and lower per-eye resolution reduces text legibility at distance.
For training applications where content focuses on procedural learning rather than fine visual detail, the Quest 3S provides compelling value. Organizations can deploy three Quest 3S units for approximately the cost of one Quest 3, dramatically expanding training capacity.
Best For: Cost-sensitive training programs, large headset fleets, onboarding and basic MR workflows, educational institutions.
Strengths:
Very low price point.
Shared Meta ecosystem with Quest 3.
Identical processor performance.
Full software compatibility.
Excellent hand tracking.
Tradeoffs:
Lower display quality with Fresnel lenses.
Reduced MR fidelity compared to Quest 3.
No depth sensor for advanced spatial mapping.
#5 Magic Leap 2: Best Optical See-Through AR
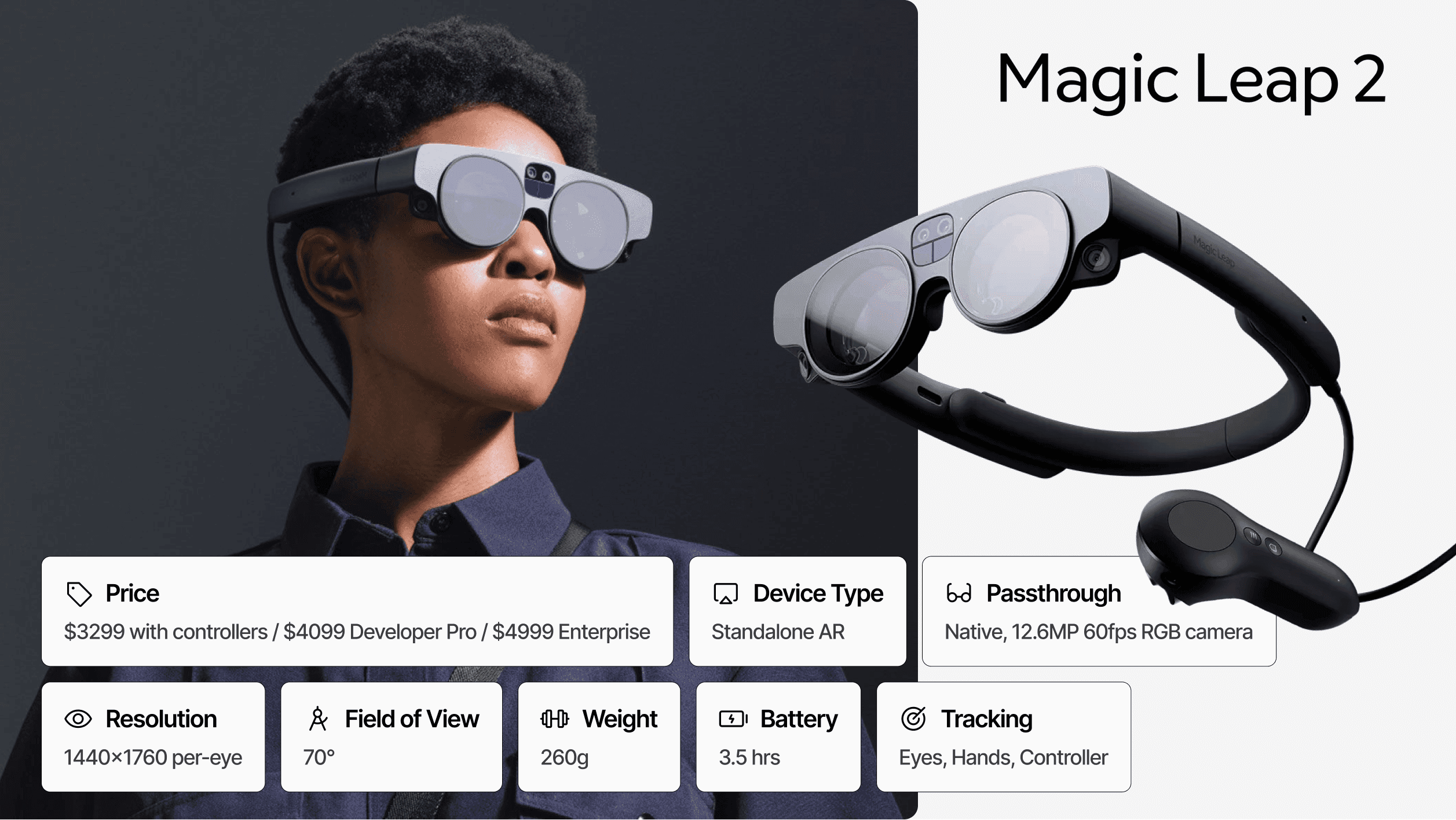
Price: $3,499 | Architecture: Tethered Compute Pack | Passthrough: Optical See-Through (Native) | Resolution: 1440 x 1760 per eye | FoV: 70° Diagonal | Weight: 260g (Headset) | Battery: ~3.5 hours
While most 2026 headsets have pivoted to video passthrough (cameras feeding screens), the Magic Leap 2 remains the gold standard for Optical See-Through AR. Instead of showing you a video of the world, it allows you to look directly through transparent lenses with digital content projected into your field of view.
This architecture solves the "safety critical" problem: if the power fails, you still see the real world instantly, not a black screen. This makes the Magic Leap 2 the preferred choice for surgical environments, active manufacturing floors, and defense scenarios where losing visual contact with reality is non-negotiable.
The device's killer feature, Dynamic Segmented Dimming, solves the ghosting issue inherent to legacy optical AR. It can selectively block real-world light behind virtual objects, making holograms appear solid and opaque, even in bright rooms, without darkening the rest of your view.
Best For: Surgical navigation, complex assembly on active factory floors, outdoor augmented reality, and safety-critical industrial defense.
Strengths:
Native Optical View: Zero latency and natural vision; safe for hazardous zones.
Lightweight Headset: At 260g (vs. ~515g+ for Quests), it is significantly lighter on the head because the battery and processor are worn on the belt (Compute Pack).
Segmented Dimming: The only optical headset that can render solid black and opaque colors.
No Motion Sickness: The direct view of reality eliminates the sensory mismatch common in video passthrough.
Tradeoffs:
Tethered Compute: Requires wearing a "puck" on your belt or shoulder.
Smaller FoV: 70° Field of View is excellent for AR, but feels restrictive compared to the 100° of VR/MR headsets.
Transparency: Cannot do full VR (opaque backgrounds) as well as video passthrough devices.
#6 HoloLens 2: Best for Microsoft-Native Enterprise Infrastructure
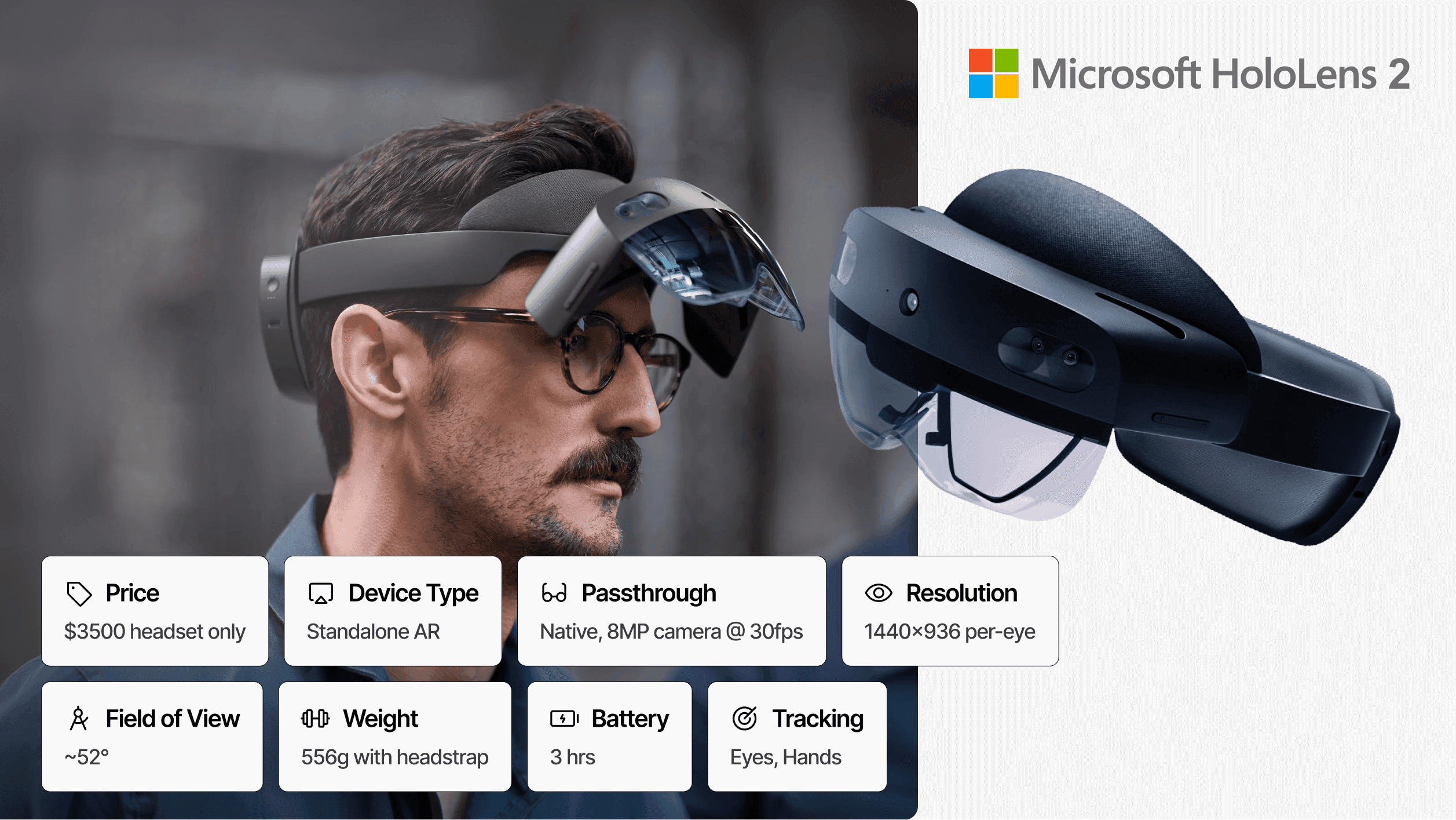
Price: $3,500 | Architecture: Standalone AR | Passthrough: Optical See-Through (Native) | Resolution: 1440x936 per-eye | FoV: 52° Diagonal | Weight: 556g | Battery: 3 hours
Microsoft HoloLens 2 remains the strategic choice for organizations deeply integrated into the Microsoft enterprise ecosystem, despite the company's announced plan to discontinue the product line.
For enterprises already running Azure cloud services, Dynamics 365, Microsoft 365, and Teams, HoloLens 2 provides turnkey integration that no competitor matches. Dynamics 365 Guides, Remote Assist, and Spatial Anchors deliver immediate productivity applications without custom development. Azure Active Directory integration, Intune device management, and enterprise-grade security align seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure and compliance requirements.
Like Magic Leap 2, HoloLens 2 uses optical see-through AR rather than video passthrough, providing inherent safety advantages for industrial environments. The native view of reality eliminates power failure risks and visual latency entirely. However, its 52° field of view is the most restrictive on this list, limiting peripheral awareness and content density.
Best For: Microsoft-standardized enterprises, Azure-integrated workflows, industrial maintenance with Dynamics 365 Guides, remote assistance scenarios.
Strengths:
Deep Microsoft ecosystem integration.
Optical see-through architecture for safety-critical work.
Mature enterprise management via Intune.
Pre-built Dynamics 365 applications.
Azure Active Directory and compliance support.
Tradeoffs:
Product line discontinued (support continues through 2027).
Extremely limited 52° field of view.
Lowest display resolution on this list.
Higher weight than dedicated optical competitors.
Uncertain long-term roadmap beyond support window.
#7 PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise: Best Low-Cost Enterprise Alternative

Price: ~$800-900 | Architecture: Standalone | Passthrough: Video (color, 32MP cameras) | Resolution: 2160 × 2160 per eye | FoV: 105° | Weight: 580g | Battery: 3-4 hours
PICO, owned by ByteDance, offers a cost-effective alternative to Meta's enterprise solutions with strong regional support in Asia and EMEA.
The PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise features dual 32MP RGB cameras for high-quality color passthrough, the Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 processor for competitive performance, and Wi-Fi 7 support for low-latency wireless streaming. The larger 5700mAh battery delivers 3-4 hours of active use, addressing a common limitation of competing headsets.
PICO Business Suite provides MDM capabilities, kiosk mode configuration, and content management tailored for enterprise deployment. The open Android-based operating system allows deeper customization than some competitors, appealing to organizations requiring modified system behaviors.
Best For: Training centers, Asia/EMEA deployments, controlled enterprise environments, budget-conscious fleet expansion.
Strengths:
Competitive pricing.
Enterprise-focused features.
Longer battery life.
High-resolution passthrough cameras.
Customizable system settings.
Tradeoffs:
Smaller application ecosystem than Meta.
Weaker global developer momentum.
Regional support limitations outside Asia/EMEA.
#8 Varjo XR-4: Best Simulation-Grade Headset
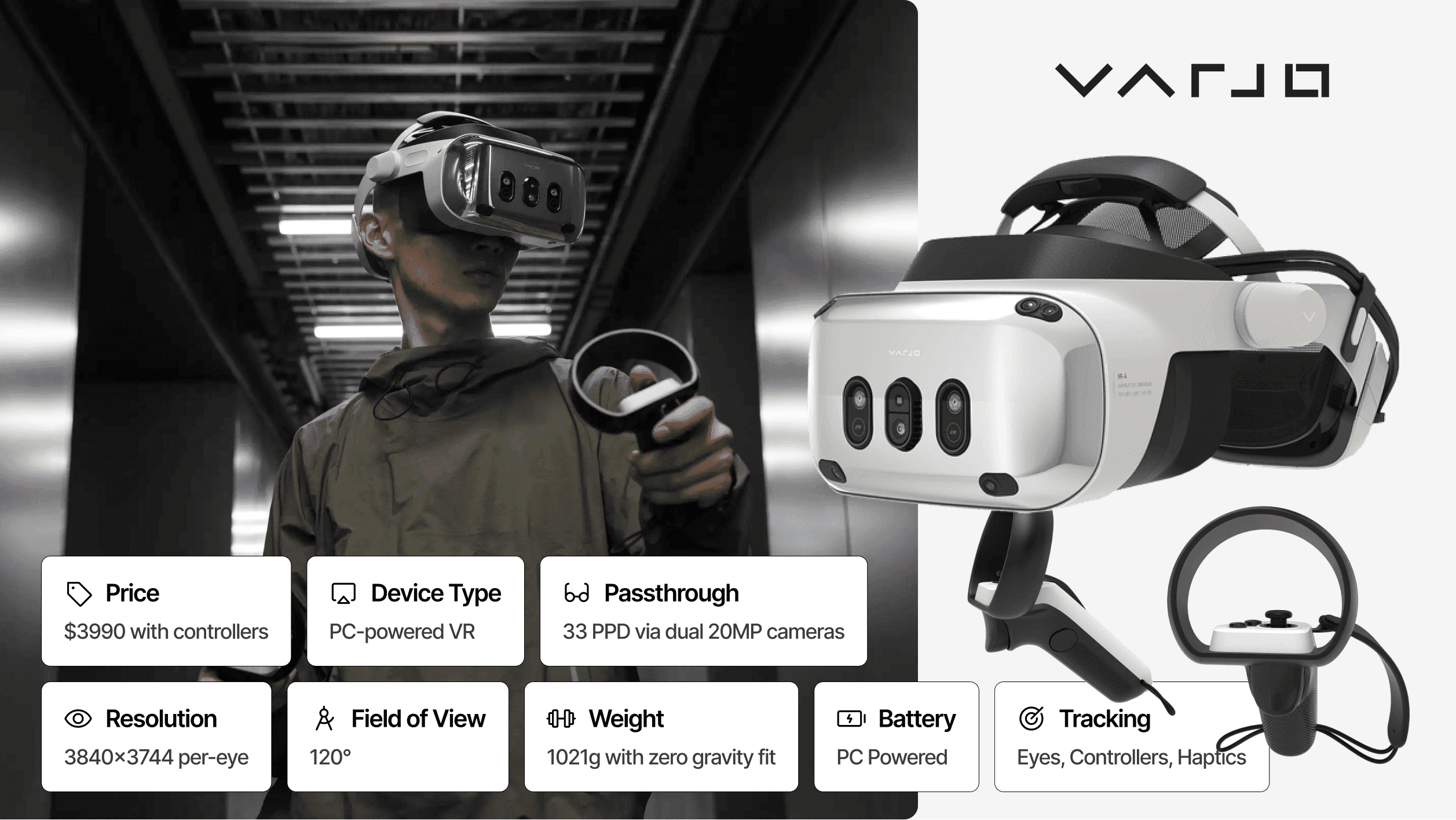
Price: Starting at $3,990 (+ software license) | Architecture: PC-tethered | Passthrough: Video (20MP cameras, up to 51 PPD) | Resolution: 3840 × 3744 per eye | FoV: 120° × 105° | Weight: ~500g | Battery: N/A (tethered)
Varjo XR-4 delivers what no standalone headset can approach: human-eye-class visual fidelity designed for mission-critical training and simulation.
The 4K-per-eye mini-LED displays achieve 51 pixels per degree in the Focal Edition, enabling trainees to read instrument panels, identify targets, and perceive fine details exactly as they would in real environments. The 120° × 105° field of view achieves full binocular vision, critical for realistic peripheral awareness in flight simulation and vehicle training.
The XR-4 Secure Edition offers TAA compliance and Finland-based manufacturing for government and defense applications requiring maximum security. Integration with over 100 professional PC applications including Lockheed Martin Prepar3D, Autodesk VRED, and NVIDIA Omniverse enables sophisticated simulation pipelines. The 200Hz eye tracking supports analytics, foveated rendering, and gaze-driven interactions.
Best For: Aerospace training, automotive simulation, medical and defense applications, scenarios requiring extreme visual precision.
Strengths:
Human-eye resolution (51 PPD).
Eye-tracked foveated rendering.
Widest field of view (120°).
Professional software integration.
TAA-compliant options.
Tradeoffs:
High cost.
Requires powerful PC infrastructure.
Setup complexity.
Narrow use-case focus.
Ongoing software license requirements.
#9 Xreal Air 2 Ultra: Best Lightweight AR Glasses for Developers
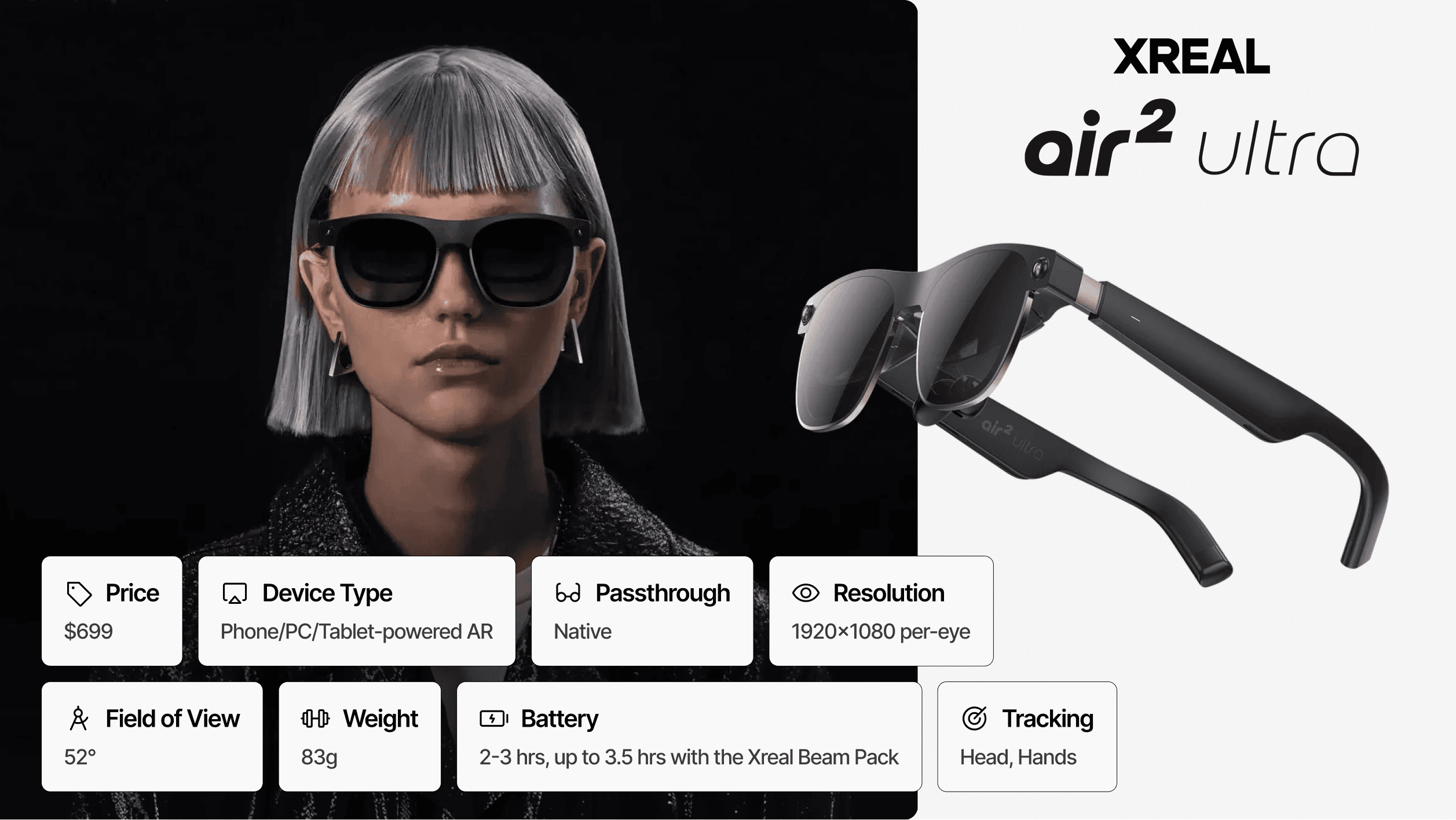
Price: $699 | Architecture: Phone-powered (USB-C tethered) | Passthrough: Optical See-Through | Resolution: 1920 × 1080 per eye | FoV: 52° | Weight: 83g | Battery: Device-dependent (phone/Beam Pro)
The Xreal Air 2 Ultra brings true spatial computing capabilities into an eyewear form factor weighing just 83 grams, less than one-sixth the weight of standalone headsets.
Unlike traditional AR headsets, the Air 2 Ultra requires tethering to a smartphone, PC, or the optional Xreal Beam Pro compute puck via USB-C. This architectural decision eliminates onboard battery and processing weight, enabling all-day wearability that no standalone device approaches. Dual 3D environment sensors provide full 6DoF positional tracking, real-time SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping), and hand tracking capabilities previously limited to bulky headsets.
The Xreal Nebula SDK enables custom mixed reality application development, making the Air 2 Ultra the primary choice for prototyping lightweight AR experiences. However, the 52° field of view restricts peripheral content visibility, and the phone-powered architecture limits deployment to scenarios where tethering is acceptable.
Best For: AR/MR prototyping, lightweight spatial computing experiences, developer testing, on-the-go productivity augmentation.
Strengths:
Exceptionally lightweight (83g vs. 515g+ for standalone).
True 6DoF tracking with depth sensors.
Electrochromic dimming without clip-ons.
Premium titanium construction.
Developer-friendly SDK.
All-day wearability.
Tradeoffs:
Requires tethered device (phone/PC/Beam Pro).
No onboard battery or processing.
Limited 52° Field of View.
Lower resolution than premium headsets.
Developer-focused; limited consumer apps.
Birdbath optics create thicker profile than regular glasses.
Best Mixed Reality Headsets by Enterprise Use Case
Different mixed reality enterprise applications demand different hardware capabilities. This section matches headsets to specific workflows, helping you identify the right tool for your organization's primary use case.
Training and Workforce Enablement
VR-based training programs have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness:
Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
Knowledge Retention | 75% better vs. traditional methods |
Training Time Reduction | 40-60% faster |
Cost Reduction (at scale) | Up to 90% vs. classroom methods |
Primary Recommendation: Meta Quest 3 offers the best combination of training application availability, device management maturity, and cost-effectiveness for most training scenarios.
Alternative: Meta Quest 3S or PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise for organizations prioritizing fleet size over individual device capability.
Design, Engineering, and Digital Twins
Design review and engineering visualization applications demand the highest visual fidelity to enable meaningful evaluation of details, proportions, and surface quality. These use cases justify premium hardware investment through reduced prototyping costs and accelerated design iteration.
Primary Recommendation: Apple Vision Pro delivers industry-leading visual precision for CAD visualization, design collaboration, and executive stakeholder presentations.
High-Precision Alternative: Varjo XR-4 for scenarios requiring absolute visual accuracy, such as automotive design finalization or aerospace component inspection.
AI-First Spatial Workflows
Organizations building AI-augmented workflows benefit from native integration between spatial computing and large language models. These applications leverage contextual awareness, conversational interfaces, and multimodal interaction to create more intuitive user experiences.
Primary Recommendation: Samsung Galaxy XR provides the deepest AI integration through Gemini, enabling conversational spatial computing that transforms how users interact with information and environments.
Simulation and Mission-Critical Visualization
Flight simulation, vehicle training, and medical procedures require visual fidelity that exactly replicates real-world conditions. For these applications, consumer-grade compromises undermine training effectiveness and can create negative transfer when trainees move to actual equipment.
Primary Recommendation: Varjo XR-4 (including Focal Edition for mixed reality cockpit training or Secure Edition for classified environments) delivers simulation-grade fidelity that justifies its premium through reduced real-world training risk and cost.
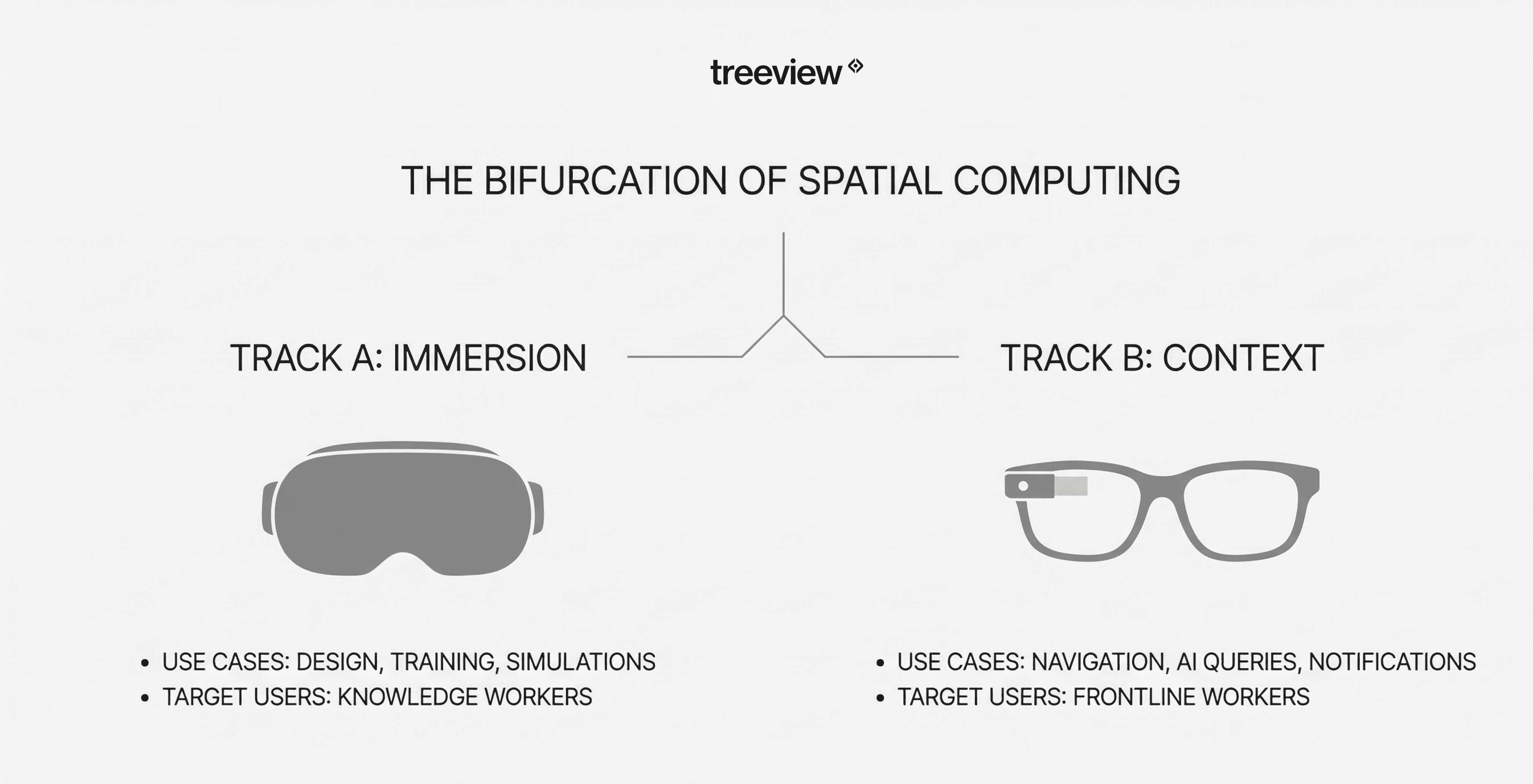
Mixed Reality Headsets vs Smart Glasses
The spatial computing industry increasingly bifurcates into two complementary categories: MR headsets for immersive spatial work and smart glasses for contextual AI assistance. Understanding this distinction helps organizations plan comprehensive spatial computing strategies.
Factor | MR Headsets | Smart Glasses |
|---|---|---|
Primary Use | Deep immersion, 3D manipulation, simulation | Contextual AI assistance, notifications |
Session Length | 15 minutes to several hours | All-day wear |
Attention Model | Dedicated, focused sessions | Ambient, continuous support |
Examples | Meta Quest 3, Vision Pro, Varjo XR-4, Magic Leap 2 | Xreal Air 2 Ultra (with 6doF tracking and spatial computing capabilities), Meta Ray-Ban, Snap Spectacles |
Forward-thinking enterprises will deploy both form factors, not choose between them. Training centers use MR headsets for immersive skill development while field technicians wear smart glasses for ongoing support. The key is matching the technology to the task's cognitive and physical demands.
How to choose a Mixed Reality Headset
There is no universal "best" mixed reality headset. The optimal choice depends entirely on your specific use case, budget constraints, and organizational context.
Use Case | Recommended Headset |
|---|---|
Most enterprises starting MR journey | Meta Quest 3 |
Premium visual fidelity | Apple Vision Pro |
Simulation-grade VR applications | Varjo XR-4 |
AI-first workflows | Samsung Galaxy XR |
Budget fleet deployment | Meta Quest 3S or PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise |
Safety-critical / Medical MR | Magic Leap 2 |
Success in enterprise MR deployment comes from matching hardware capabilities to specific business problems, investing in quality content development, and managing organizational change effectively. Focused deployments with clear success metrics consistently outperform strategies that wait for "perfect" technology.
The mixed reality market continues rapid evolution, with new hardware announcements expected throughout 2026. However, organizations that begin building spatial computing capabilities today will be better positioned to adopt next-generation technology than those waiting on the sidelines.
Enterprise Buying Checklist
Successful MR deployment requires preparation beyond hardware selection. This checklist covers critical factors that determine whether your mixed reality investment delivers ROI or becomes expensive shelf decoration.
Before purchasing Hardware
Secure access to Mixed Reality Development expertise: Through internal teams or partnerships with mixed reality studios and mixed reality development companies, ensure you have the design, 3D, and software engineering capabilities to create compelling content. Hardware without quality content delivers no value. Treeview and similar mixed reality partners can provide the specialized expertise required for enterprise-grade implementations.
Define one measurable KPI: Whether reducing training time, improving error rates, or accelerating design cycles, establish a clear success metric before deployment. Without defined outcomes, MR projects drift toward technology showcases rather than business impact.
Validate comfort with high-quality pilots: Run small-scale trials with actual end users to assess fit, comfort over intended session lengths, and any motion sensitivity issues before committing to fleet purchases.
Assess environment constraints: Consider lighting conditions, physical space requirements, Wi-Fi infrastructure, and safety regulations that might affect headset selection or deployment locations.
Confirm MDM and Security requirements: Verify that chosen headsets integrate with your existing device management infrastructure and meet organizational security policies.
Plan your content pipeline: Determine whether you will use off-the-shelf applications, customize existing solutions, or develop custom content. Each approach has different timeline and resource implications.
After purchase and deployment
Software integration: Connect MR applications with existing enterprise systems like LMS, ERP, or CRM to maximize data value and workflow continuity.
Change management: Develop training programs that help employees become comfortable with MR technology and understand its value to their work.
Adoption strategy: Plan phased rollouts that build internal champions and allow iterative improvement based on user feedback.
Remember: Hardware enables mixed reality, but software determines ROI. The best headset paired with poor content delivers worse results than a budget headset with excellent applications tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Mixed Reality Headsets
Q1. What is a mixed reality headset?
A mixed reality headset is a wearable device that blends digital content with the physical world, allowing users to interact with virtual objects that appear anchored to real-world surfaces. Unlike pure VR headsets that fully immerse users in virtual environments, MR headsets use cameras and sensors to create a composite view where digital and physical elements coexist and interact.
Q2. Is mixed reality the same as augmented reality?
Mixed reality and augmented reality overlap but are not identical. Augmented reality typically overlays 2D information onto the real world (like smartphone AR filters or heads-up displays), while mixed reality creates 3D virtual objects that interact with physical surfaces and can be occluded by real-world objects. MR provides deeper spatial integration and more realistic interactions.
Q3. Is mixed reality the same as spatial computing?
Spatial computing is the broader category that encompasses mixed reality, virtual reality, and augmented reality. Think of spatial computing as the umbrella term for any technology enabling human-computer interaction in three-dimensional space. Mixed reality is one interaction model within this category.
Q4. Do mixed reality headsets require controllers?
Modern MR headsets support multiple input methods. Most offer hand tracking that recognizes gestures without physical controllers, making them suitable for applications where hands must remain free. Controllers remain valuable for gaming-style interactions and applications requiring precise pointing. The best headsets support both options.
Q5. What is the best mixed reality headset overall?
The Meta Quest 3 currently offers the best overall balance of MR capability, cost, and ecosystem maturity for most enterprise applications. However, "best" depends entirely on use case: Apple Vision Pro leads for design visualization, Varjo XR-4 dominates simulation, and Samsung Galaxy XR excels for AI-integrated workflows.
Q6. Which MR headset is best for enterprise use?
For most enterprises starting their MR journey, Meta Quest 3 provides the optimal combination of capability, cost, and scalability. Organizations with specific needs may prefer Apple Vision Pro (design/engineering), PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise (budget fleet deployment), or Varjo XR-4 (simulation/training requiring highest fidelity).
Q7. Are mixed reality headsets worth the investment?
For appropriate use cases, yes. Enterprise studies demonstrate training cost reductions up to 90% versus traditional methods, knowledge retention improvements of 75%, and training time reductions of 40-60%. However, ROI depends on proper use-case selection, quality content development, and effective change management.
Q8. How long do MR headsets last?
Enterprise-grade MR headsets typically have a useful lifespan of 3-5 years before technology advances or component wear necessitates replacement. Battery degradation may reduce effective battery life over time. Proper storage, cleaning, and handling extend device longevity significantly.
Q9. Optical see-through vs video passthrough: which is better?
Video passthrough dominates current MR headsets due to superior virtual content integration and improving latency. Optical see-through preserves natural visual response but limits display brightness and contrast. For most enterprise applications, video passthrough provides better overall mixed reality experiences.
Q10. Do MR headsets work offline?
Most standalone MR headsets can run local applications offline after initial setup and content download. However, features requiring cloud processing, real-time updates, or multi-user collaboration need network connectivity. Enterprise deployment should plan for both online and offline scenarios.
Q11. What data do MR headsets collect?
MR headsets collect spatial data about the user's environment, eye and hand tracking information, and usage analytics. Enterprise deployments should review each manufacturer's privacy policies, enable appropriate data controls, and ensure compliance with organizational security requirements and applicable regulations.
Q12. Can MR be used in hazardous environments?
Consumer MR headsets are not safety-certified for hazardous environments. Specialized industrial solutions exist for specific applications, but organizations must verify certifications appropriate to their environment (e.g., intrinsic safety ratings for explosive atmospheres) before deployment.
Q13. Can multiple users share one device?
Most enterprise-focused headsets support shared-device modes with multiple user profiles, essential for training centers and shift-based operations. Features vary by device; verify specific capabilities including user switching speed, profile isolation, and hygiene management options.
Q14. How much do MR headsets cost?
Enterprise MR headset pricing ranges widely: Meta Quest 3S starts at $299, Meta Quest 3 at $499, PICO 4 Ultra Enterprise around $800, Samsung Galaxy XR at $1,799, Apple Vision Pro at $3,499, and Varjo XR-4 from $3,990 plus software licensing. Total cost of ownership includes content development, device management, and support.
Q15. What is the typical ROI timeline?
Organizations with focused use cases and quality implementation typically see positive ROI within 12-18 months for training applications. Design and engineering applications may show faster returns through reduced prototyping costs. Broad experimentation without defined objectives rarely achieves positive ROI.
Q16. Is MR cheaper than traditional training?
For applications involving high-risk scenarios, expensive equipment, dispersed workforces, or frequently updated procedures, MR training often costs less than traditional alternatives when scaled appropriately. Studies show training cost reductions up to 90% for suitable use cases.
Q17. Can you recommend a good mixed reality development agency?
Leading mixed reality development companies and mixed reality studios like Treeview specialize in enterprise-grade spatial computing solutions, bringing together design, 3D development, and software engineering expertise. When evaluating mixed reality agencies, look for enterprise deployment experience, portfolio diversity, and technical capabilities matching your specific needs.
Q18. Who should I hire to build a mixed reality app?
For enterprise mixed reality applications, consider:
Mixed reality agencies for full-service development.
Mixed reality studios for focused creative execution.
Mixed reality custom app developers for bespoke solutions.
Mixed reality consultants if you need strategic guidance first.
The best mixed reality developers like Treeview combine technical platform expertise with understanding of enterprise requirements like security, scalability, and system integration.
Q19. Where can I find mixed reality developers?
Mixed reality developers can be found through specialized XR studios, enterprise technology consultancies, and talent platforms. For complex enterprise projects, working with established mixed reality development companies like Treeview often proves more effective than assembling individual contractors, due to the multidisciplinary nature of spatial computing projects.
Q20. What should I look for in a mixed reality developer?
Evaluate mixed reality developers based on:
Experience with your target platform (Meta Quest, Vision Pro, etc.).
Understanding of enterprise requirements (security, scalability, integration).
3D design and Unity specialist capabilities.
Proven ability to deliver production-ready applications.
Portfolio review and reference checks matter more than technical certifications alone. The best mixed reality experts demonstrate both technical depth and business outcome orientation.
Q21. Who works with enterprise clients on mixed reality?
Top mixed reality agencies, mixed reality firms, and mixed reality service providers that focus on enterprise clients typically offer:
MDM and security integration expertise.
Change management and adoption support.
ROI measurement and optimization.
Ongoing support and content updates.
Ask potential mixed reality partners for enterprise client references and case studies demonstrating measurable business outcomes.
Q21. What companies specialize in mixed reality development?
Companies specializing in mixed reality development include dedicated mixed reality studios, enterprise technology consultancies with XR practices, and platform-specific specialists. Top mixed reality development companies like Treeview focus exclusively on spatial computing, while larger consultancies may offer MR as part of broader digital transformation services.
Q22: Who are the best mixed reality companies?
The best mixed reality companies are Treeview (Best MR Development Studio), Meta (Best MR Hardware Ecosystem), Unity (Best MR Development Platform), JigSpace (Best MR Solution), Resolution Games (Best MR Gaming & Entertainment Company).


