Everything You Need to Know about Augmented Reality in 2026
In this augmented reality complete guide, we’ll explain what AR technology is and how it combines digital elements with the physical world. You’ll learn about the technologies functionality, history, types, every day applications, and future trends. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the technologies potential and how it’s reshaping the way we interact with technology and the world around us.
What You Need to Know
Augmented Reality (AR) combines digital elements with the physical world, creating an interactive digital experience where virtual content is integrated into physical environments in real time, enhancing how users perceive and interact with their surroundings.
Key applications of AR cover a wide range of sectors, including consumer, enterprise, and government, transforming how humans engage with technology and digital content.
Major tech companies like Google, Apple, Microsoft, ByteDance (TikTok) and Meta are heavily investing in new AR hardware and infrastructure, unlocking advanced capabilities and creating extensive business opportunities across industries.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
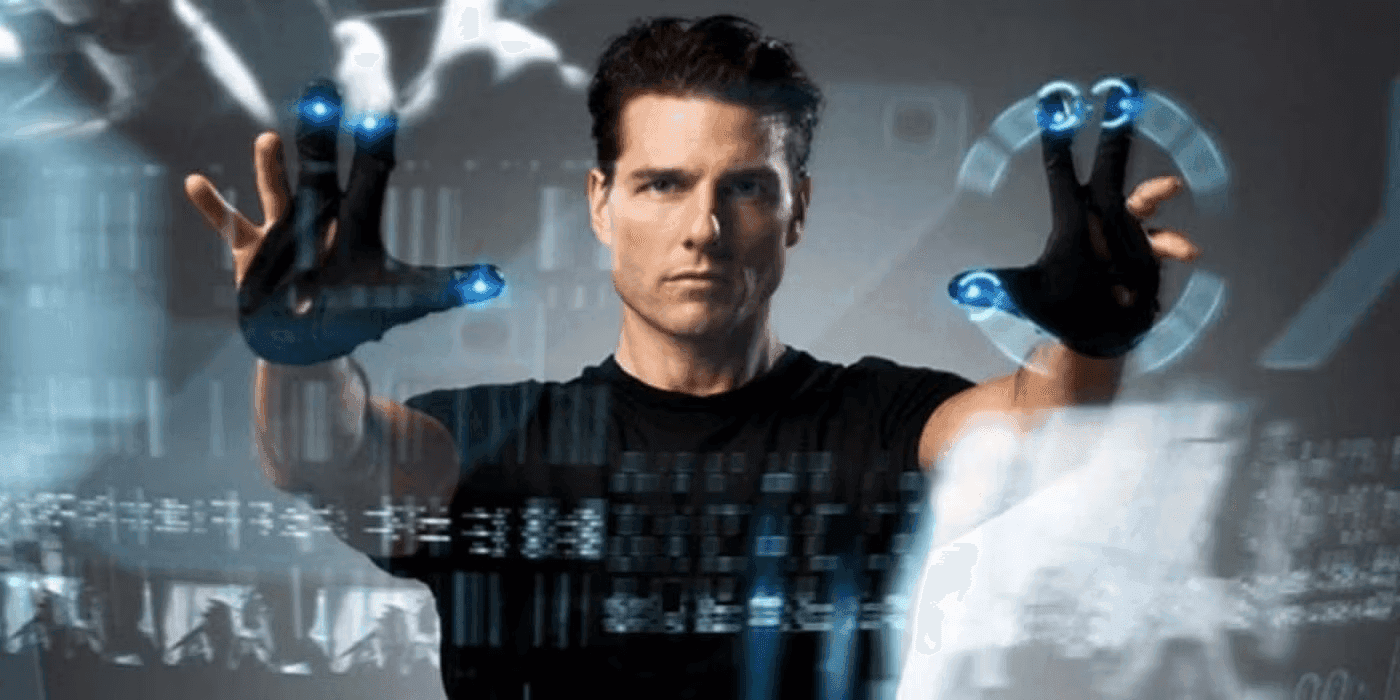

Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes digital elements, such as virtual screens, 3D models, or interactive graphics, onto the physical world. While users stay present in their physical environment, this overlaid digital content enriches their perception of reality.
Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which completely immerses users in a digital simulation by replacing their entire physical reality, AR adds digital layers to what users already see. This fundamental difference allows people to stay grounded in their physical surroundings while interacting with virtual objects that appear to exist within physical space.
Augmented reality is a subset of spatial computing (also known as XR or Extended Reality), the broader technology category that enables humans to interact with computers in three-dimensional spaces. AR sits alongside VR under this unified category that's reshaping human-computer interaction.
Core Characteristics
Key characteristics that define augmented reality include one or more of the following:
Digital overlay: Virtual elements are added to the user's view of the physical world, from simple text displays to complex animated 3D objects.
Real-time interaction: Dynamically responds to user inputs or environmental changes, allowing virtual content to adapt instantly to current context.
Spatial anchoring: AR systems anchor virtual objects to specific locations in the real world, maintaining their position relative to physical objects.
Environmental understanding: AR platforms recognize physical surfaces, lighting conditions, and spatial relationships to render realistic virtual content.
Contextual awareness: Digital elements relates to or enhances the user's current physical environment or activity.
History of Augmented Reality
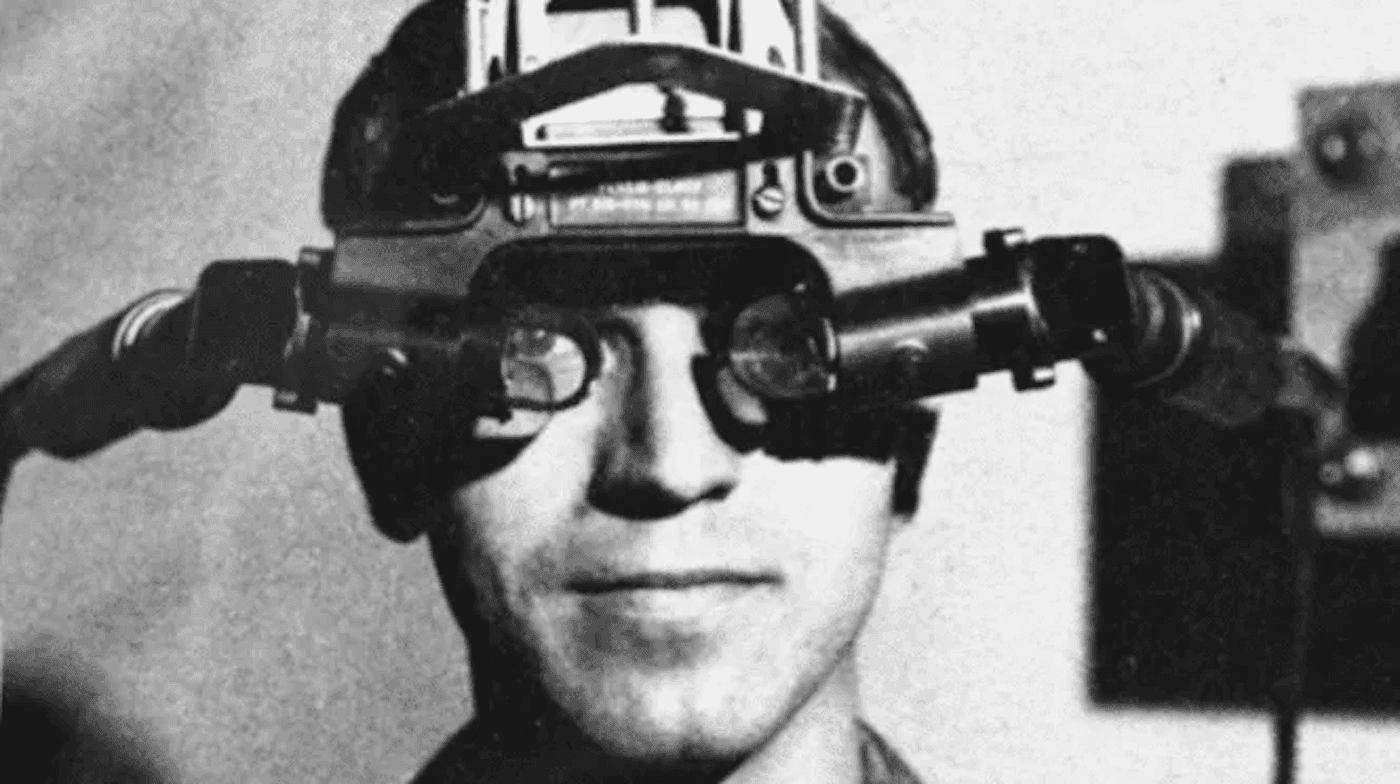

The journey of Augmented Reality includes significant milestones:
1968: Ivan Sutherland created the first AR-like system known as a head-mounted display(HMD).
1990: The term ‘augmented reality’ was coined by Tim Caudell, a researcher at Boeing.
1992: Louis Rosenburg developed ‘Virtual Fixtures’, one of the earliest fully functional AR systems used by the military.
2000: Hirokazu Kato introduced the ARToolKit, which became a fundamental tool for early AR developers.
2014: Google Glass was launched as one of the first widely publicized AR glasses, introducing a hands-free, heads-up display that overlaid digital information onto the real world. Google Glass showcased the potential of wearable AR devices and paved the way for future innovations in the field.
2016: Microsoft released HoloLens, an advanced mixed reality headset that combines augmented and virtual reality elements, offering immersive experiences for industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and education.
2017: Apple launched ARKit, a mobile AR development platform for iOS devices that enabled developers to create advanced mobile AR experiences.
2018: Magic Leap released its first mixed reality headset, introducing an advanced head-mounted display with groundbreaking hardware technology that significantly influenced the development of AR devices and set new standards for hardware in the field.
2021: Facebook rebranded to Meta, signaling a major strategic shift towards becoming the leader in the next computing platform that integrates augmented and virtual reality technologies.
2024: Apple launches the Vision Pro, a high-end AR headset combining advanced hardware and software to deliver immersive mixed reality experiences, marking a historic milestone in AR technology development.
2025: Google launched AndroidXR, entering the AR hardware market in collaboration with Samsung, marking a significant expansion in augmented reality with AI capabilities and use cases.

How Does Augmented Reality (AR) Work?
At its core, augmented reality relies on hardware like head-mounted displays with sensors and cameras, combined with advanced software techniques such as computer vision, spatial mapping, simultaneous localization, and object recognition.
These technologies enable digital elements to blend seamlessly with the digital and physical worlds, anchoring virtual objects to real-world objects and creating immersive AR experiences that respond naturally to user interactions.
Types of Augmented Reality Experiences
There are a lot of different types of AR experiences available today, a few of which include:
Mobile AR: Uses smartphones and tablets with cameras and sensors to deliver augmented reality apps. It includes Marker-based AR, which uses visual markers like QR codes for digital overlays, and Markerless AR, which relies on device sensors and computer vision to place virtual objects in real-world environments without markers.

Optical Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): These are wearable devices, such as smart glasses, that overlay digital elements directly onto the user's field of vision, allowing interaction with virtual elements in the real world while the user still sees their actual physical surroundings.
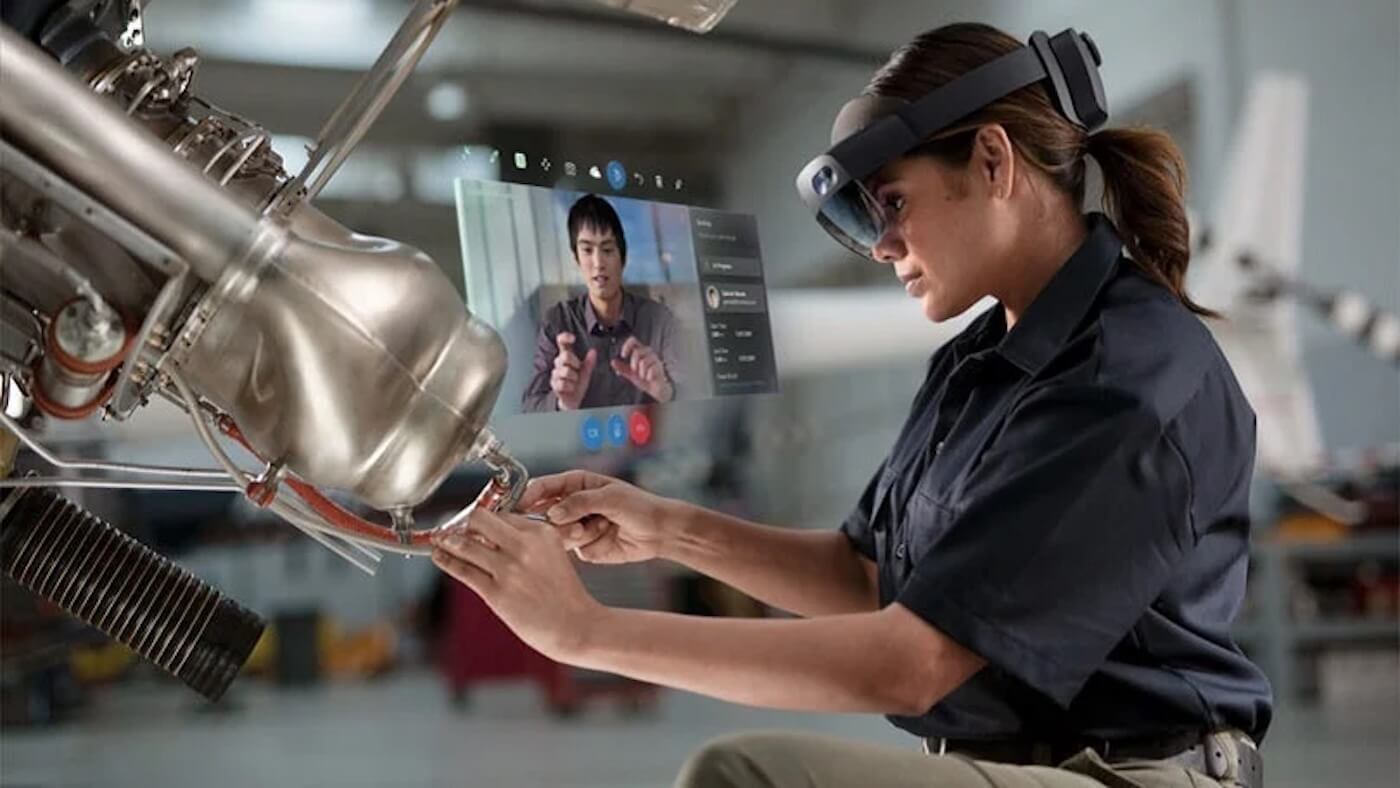

Screen Pass-through HMDs: These devices use external high-quality cameras to capture the real world and display it on internal screens with added digital overlays. The camera quality is so advanced that users cannot perceive they are looking at screens, providing an immersive augmented reality experience while maintaining awareness of the physical environment.
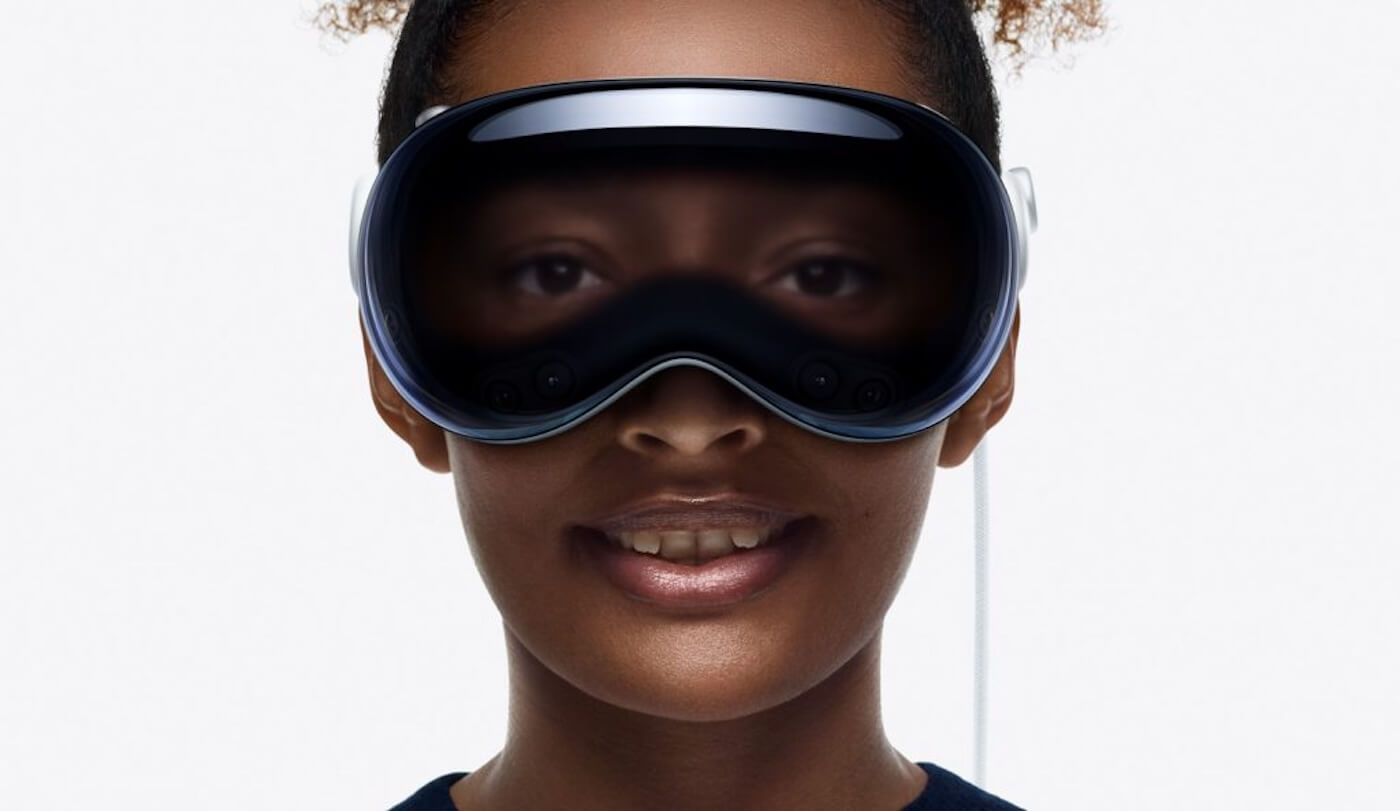

Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (VR) are often mentioned together, but they offer fundamentally different experiences. AR enhances the real-world experience by overlaying digital elements, allowing users to retain control of their real-world presence. In contrast, VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment, often isolating them from their physical surroundings.
AR and VR differ in several key ways:
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, allowing users to see and interact with virtual objects while remaining aware of their physical environment.
Virtual Reality (VR) creates a fully immersive digital environment that replaces the user's real-world surroundings, typically experienced through specialized headsets.
AR enhances the real world by blending virtual elements with physical surroundings, enabling interactive experiences that complement reality.
VR immerses users in a completely virtual world, isolating them from the physical environment.
AR is generally more accessible and versatile, as it can be used on common mobile devices and supports a wide range of applications, while VR requires dedicated hardware.
Primary AR Hardware and Software Companies
To create augmented reality applications, three key parts are essential: hardware, software development platforms, and a skilled AR app development team.
Together, these companies form the foundation of successful augmented reality app development, enabling the creation of high-value AR use-cases across many industries.
For more details see our list of the most important companies in the augmented reality industry or virtual reality industry.
Augmented Reality Hardware Companies
Here is a list of leading AR hardware currently available on the market:
Apple Vision Pro: Apple's flagship spatial computing headset offering advanced AR experiences with industry-leading display technology.
Meta Quest 3/3S: Meta's latest headsets combining affordability with lightweight design, high-resolution displays, and powerful processing for versatile applications.
Magic Leap 2: An advanced AR headset designed for enterprise use, featuring improved optics and computer vision capabilities.
Microsoft HoloLens 2: A device widely used in industries like healthcare and manufacturing for hands-free AR interaction.
Snap Spectacles: Lightweight AR glasses designed for social media and augmented reality experiences on the go.
PICO: A Chinese AR/VR headset offering competitive hardware for both consumer and professional markets.
Augmented Reality Software Development Platforms
AR app development platforms are the essential tools that enable developers to create augmented reality apps. The leading platforms include:
Unity: A powerful and versatile cross-platform 3D engine widely used for AR development. Unity supports multiple AR SDKs and offers a ecosystem for creating augmented reality applications compatible with all platforms.
Unreal Engine: Known for its high-fidelity graphics and real-time rendering capabilities, Unreal Engine is another popular choice for AR app development. However, it is less versatile compared to Unity and often lags behind in supporting the latest AR features and emerging platforms.
Platform Native Tools: These include development environments tailored to specific hardware, such as Apple’s Xcode for Vision Pro, Google Android Studio for AndroidXR, and Snapchat’s Lens Studio for creating AR lenses and effects within the Snapchat app and Spectacles.
Augmented Reality App Development Companies
Successful augmented reality app development relies heavily on skilled multidisciplinary AR development teams. These development teams cover a wide range of independent skills including 3D designers, 3D animators, technical artists, spatial UX/UI designers, software engineers, and AR industry consultants.
These roles generally fall into three key areas: Product Design, 3D content creation, and software engineering, with teams working closely together to deploy successful projects.
Key players in the AR app development industry include:
Treeview: Specializes in creating high-quality augmented reality applications for business, R&D, and innovation use cases. Treeview offers a full suite of AR development services focused on enterprise clients and is recognized as one of the world’s leading AR studios for enterprise-grade solutions.
Arcadia: Specializes in AR experiences for entertainment marketing and fan engagement. Arcadia offers AR development services focused on major marketing campaigns for top global brands.
Resolution Games: Specializes in AR game development. Known for combining engaging gameplay with the latest AR technology. Their projects range from mobile AR titles to games designed for platforms like the Meta Quest and Apple Vision Pro.
These teams work closely with clients to create custom AR applications that drive business value across various industries. For more details of AR/VR app development teams see our list of best augmented reality developers or best virtual reality developers. For platform specific AR development companies see: Top Vision Pro Developers and Top Android XR Developers.
Everyday Augmented Reality Examples
AR technology has become increasingly integrated into our daily lives through familiar applications and experiences that many users encounter regularly. Here are some great examples of AR technology:
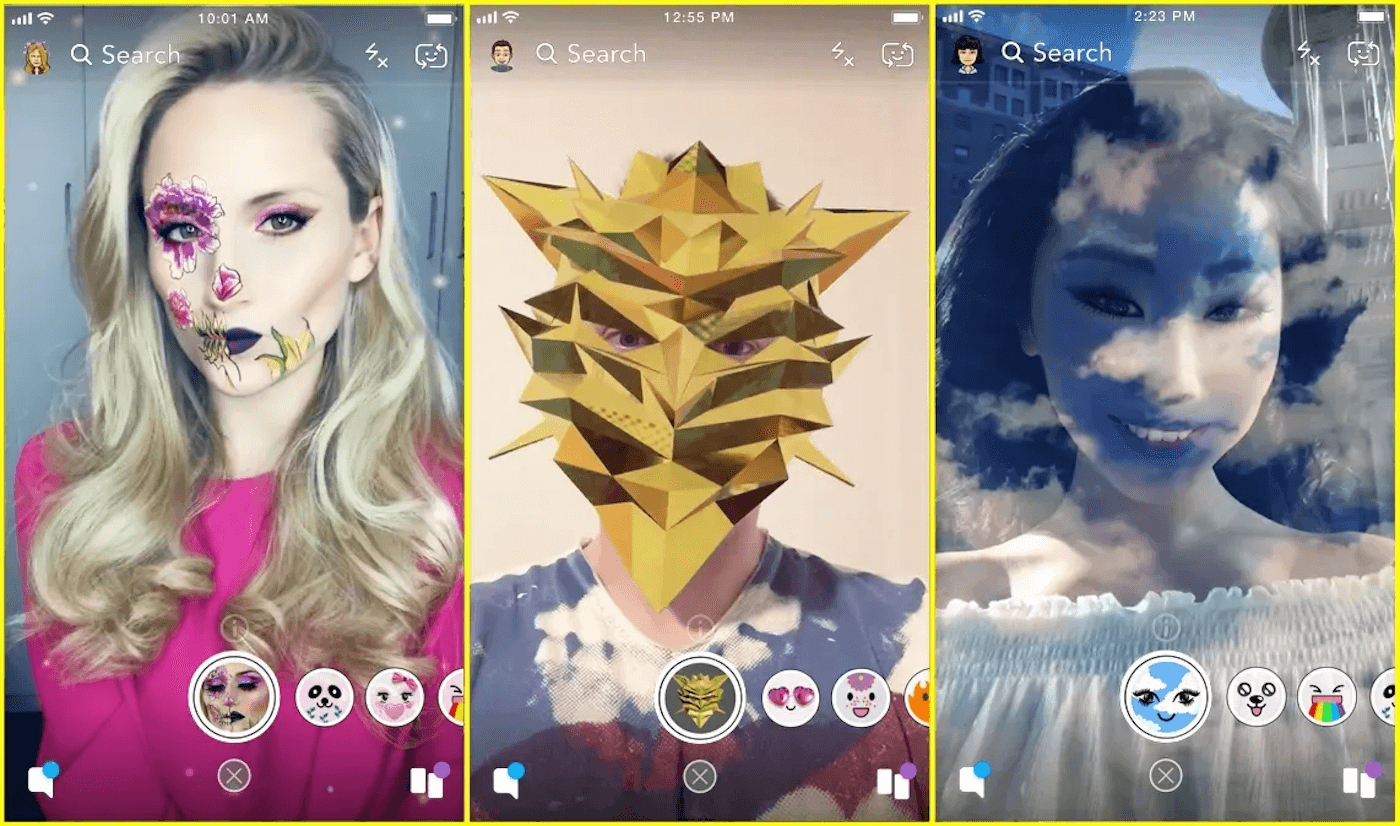
Social Media AR Filters: Platforms like Snapchat and Instagram use augmented reality filters to let users add virtual elements to selfies and videos. These range from simple face decorations to complex environmental effects, providing fun and engaging ways to enhance social media AR content.
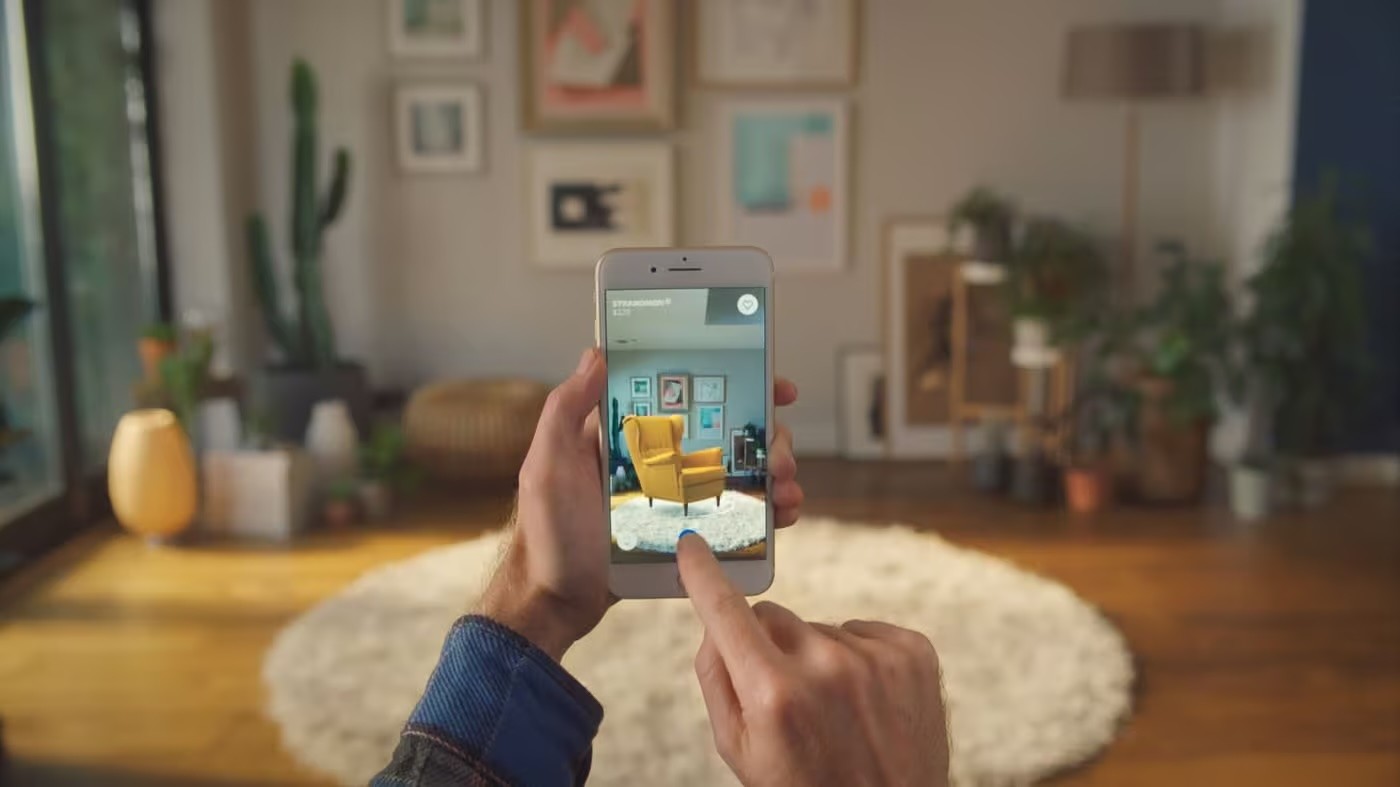
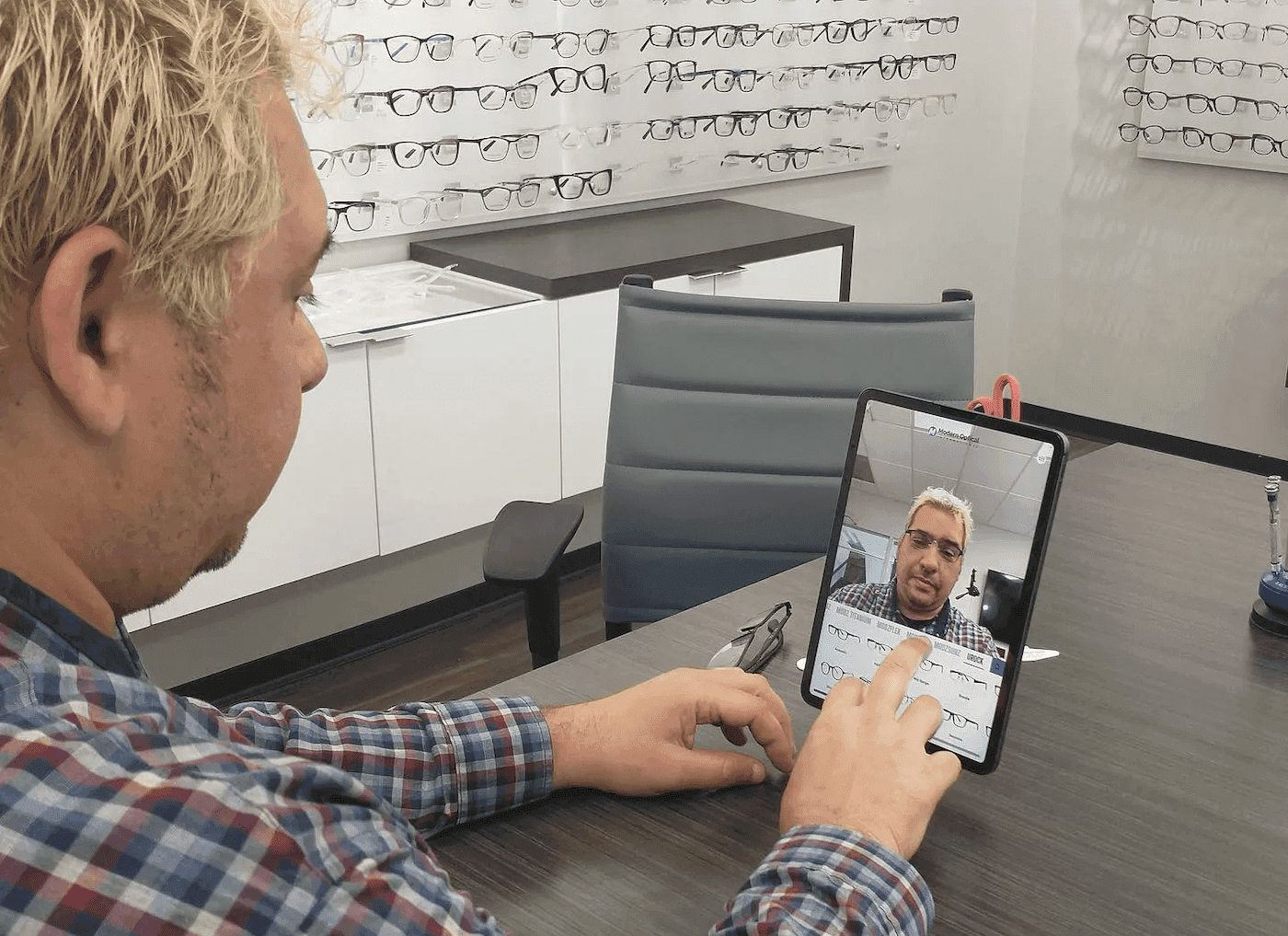
AR Virtual Try-On and Retail: Virtual try-on augmented reality apps like OCHO Vision allow customers to visualize eyewear on their faces and capture optical eye measurements. IKEA Place enables users to see how furniture fits and looks in their homes before purchasing, while ULTA Beauty’s virtual try-on features let customers test makeup products.
These retail applications powered by AR technology enhance shopping customer experiences by allowing consumers to interact with products virtually, offering advanced product visualization that helps customers make informed purchasing decisions.

Navigation and AR Maps: Automotive brands like Mercedes-Benz use AR navigation to display turn-by-turn directions directly onto the road, while BMW overlays lane guidance onto windshields.
Google Maps offers augmented reality walking directions and AndroidXR map features, providing directional overlays and immersive navigation experiences for pedestrians.

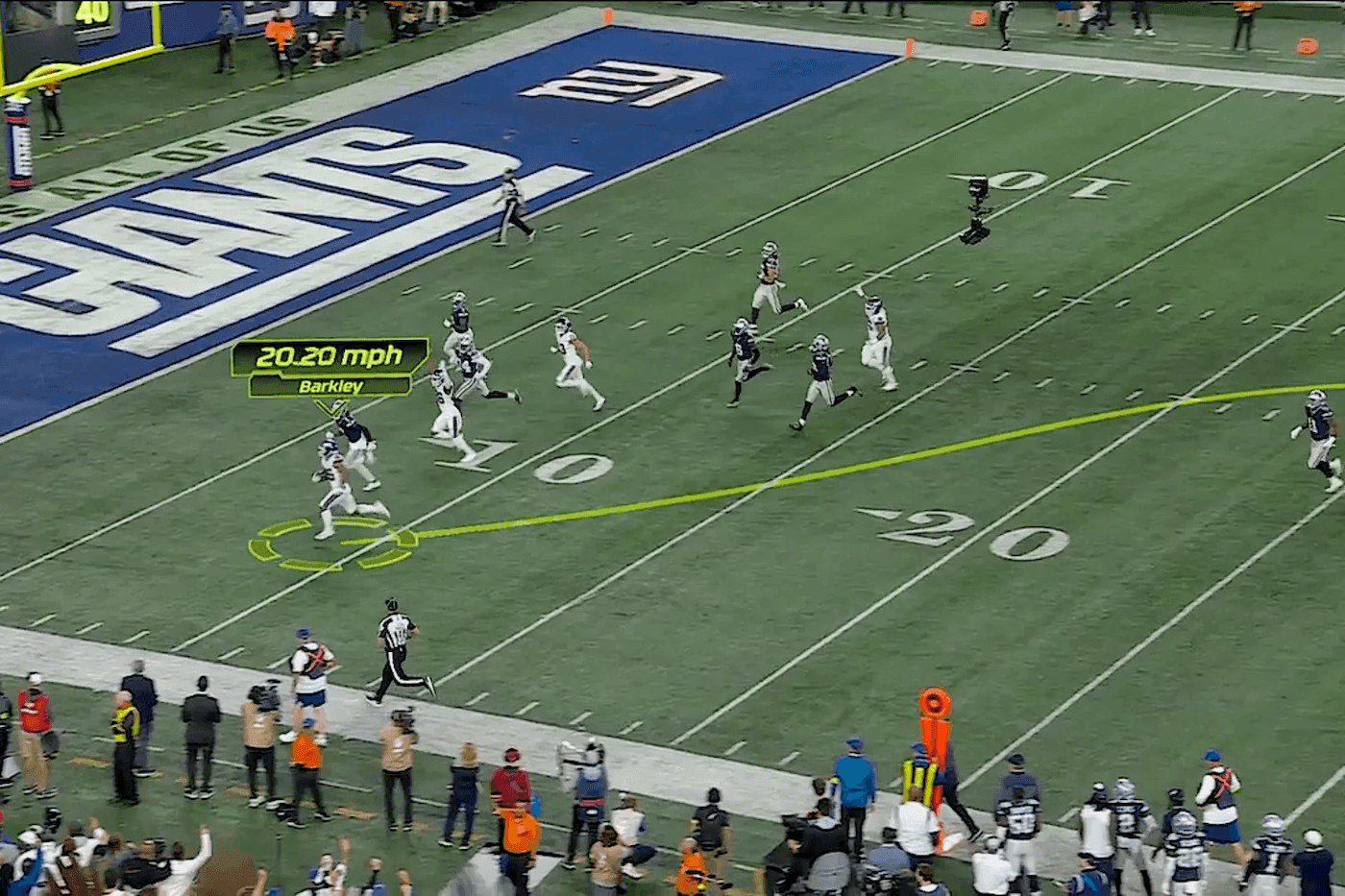
Live Sports TV Graphics: Augmented reality enriches live sports broadcasts by overlaying real-time statistics, first-down lines in football, and player tracking data directly onto game footage. Millions of viewers enjoy these enhanced visualizations, which add context and excitement to the viewing experience.
Gaming Applications: Augmented reality has introduced a new category in the gaming industry by blending digital worlds with real-world environments, creating immersive and interactive gaming experiences.
Popular games like Pokémon GO have demonstrated how AR can engage players by integrating virtual Pokémon into physical locations, encouraging exploration and social interaction.
Enterprise Applications: Beyond consumer use, AR technology plays a key role in innovation in enterprise sectors such as healthcare, AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction), heavy industry, scientific research, and data visualization.
Training augmented reality solutions enable employees and professionals to practice complex tasks in a safe, simulated environment, improving skills and reducing errors.
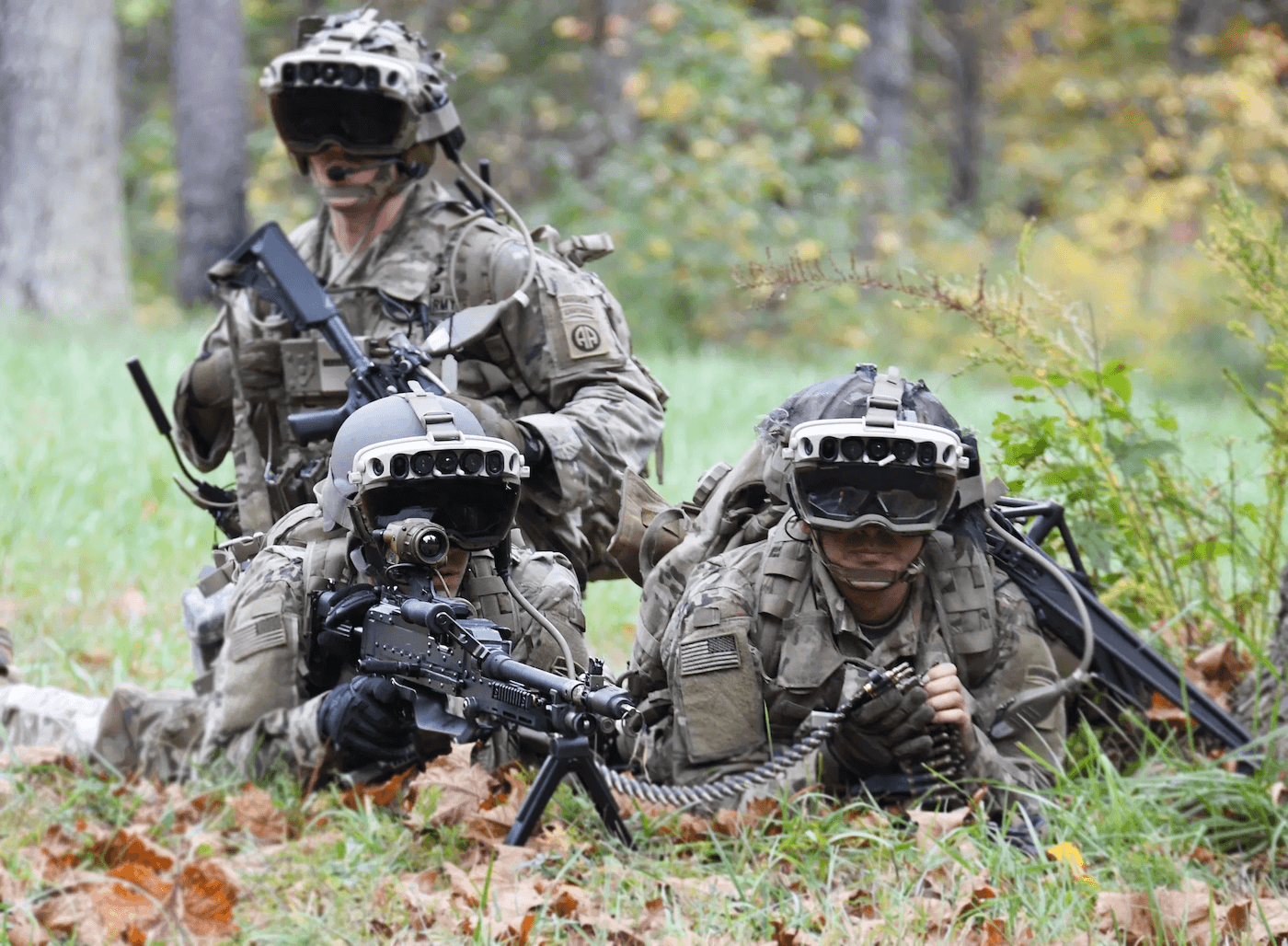
Military Applications: The military uses AR for enhanced situational awareness and training simulations, with companies like Anduril and Palantir leading military innovation.
These recent developments highlight the global focus on defense technology advancement, demonstrating AR's broad applicability across critical fields.

Developing Augmented Reality Applications
Developing an augmented reality (AR) application involves a structured development process that combines hardware, software, and design to deliver high-impact AR experiences.
Here’s a step by step guide of the key stages involved in implementing augmented reality effectively:
1. Define Vision and Business Objectives
Begin by identifying the specific business problem or opportunity the AR software will address. Understand your target audience and define clear business goals to guide the design and development process and ensure the application delivers business value.
2. Choose AR Hardware and Software Platforms
Select the appropriate AR hardware such as Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest, and AndroidXR devices based on the business context, target users, and use-case required capabilities.
3. Concept Design
The concept design phase ensures all stakeholders align on the app’s vision scope and functionalities. Clear visual communication defines core objectives, audience, and key features, creating a shared understanding that guides development and meets stakeholder, business and user needs.
4. UX/UI Design
Design beautiful and intuitive user interface that integrates virtual elements seamlessly with real world environments. Focus on spatially and diagenetic interface design principles to ensure natural interaction with content anchored in physical space.
5. 3D Content Creation
Create high-quality 3D models, animations, and interactive elements that will be overlaid on real-world surfaces. The 3D content should be optimized for AR, ensuring performance and realism to enhance user engagement.
5. Software Development and System Integration
Build the app's front-end, user interactions, features, and core capabilities using programming languages like C# and frameworks like Unity. Integrate with client backends, analytics platforms, and other use-case specific software systems as required.
6. Testing and Use-Case Validation
Test the AR application across multiple devices and environments to validate AR performance. Conduct user testing to ensure business requirements are met and resolve any compatibility or interaction issues.
7. Deployment and User Feedback
Launch the AR app to your early group of your target audience and collect insights on user behavior, app understanding and preferences. Use feedback to polish the software, fix issues, and improve usability.
8. Maintenance and Scaling
Regularly update the AR app to maintain compatibility with new hardware and software versions. Scale your AR solution by adding more users, new features, leveraging new technologies in AI and computer vision, and optimizing for extended use and new use cases.
Implementation Challenges
AR app development projects often face challenges such as working with non-senior teams or the difficulties of assembling experienced in-house AR development team.
These challenges can be overcome by partnering with a senior AR development team like Treeview, which brings the expertise and experience necessary to deliver high-quality AR technology solutions.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality

The future of augmented and virtual reality is highly promising, with the market projected to reach $200 billion by 2030. Advances in hardware and artificial intelligence unlock new use-cases and enhance AR’s rendering, tracking, battery life and processing capabilities, while new AR design languages improve user interactions, retention, and allow users to experience AR more naturally.
Leading technology companies such as Meta, Google, Apple, and Bytedance are investing heavily in augmented reality and spatial computing. These industry leaders recognize that augmented and virtual reality technologies are the next major human computing platform, following the smartphone and personal computer before them.
Today's leaders are shaping the industry that will define the next human computing interface paradigm.
Summary
In summary, Augmented Reality is revolutionizing how we interact with the world by blending digital content with our physical environment.
From entertainment and retail to healthcare and education, AR is enhancing experiences, improving efficiency, and unlocking new possibilities across industries.
As technology advances and adoption grows, AR’s potential to transform everyday life and business continues to expand, making it a key driver of the future digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances your world by overlaying digital elements onto the physical environment, making experiences more interactive and engaging.
How is Augmented Reality different from Virtual Reality?
Augmented Reality enhances your real-world experiences by overlaying digital elements onto your surroundings, while Virtual Reality immerses you in a fully immersive digital world.
What are some key applications of AR technology?
AR technology is transforming industries like retail, healthcare, education, manufacturing, automotive, real estate, tourism, entertainment, aerospace, defense, logistics, construction, agriculture, finance, marketing, sports, hospitality, energy and mining by enhancing experiences and improving efficiency.
What are the limitations of Augmented Reality technology?
The primary limitation is the lack of universal applications that provide broad utility across diverse use cases. AR currently lacks its "killer app" equivalent to Word/Excel/PowerPoint or Instagram/WhatsApp that drove mass adoption of PCs and smartphones.
Privacy concerns are also a significant challenge, as AR devices collect intimate biometric and behavioral data including eye movements, spatial behavior, and attention patterns that could reveal sensitive personal information from the user and people around them.
Who are best Augmented Reality (AR) app and Augmented Reality (AR) experience designers?
When seeking the best augmented reality app and experience designers, Treeview stands out as a leading choice in the industry. Specializing in high-quality AR applications for enterprise clients, Treeview offers full suite of AR development services from concept design to system integration. Their expertise in both technical AR development and business applications enables them to deliver world-class, scalable solutions that drive measurable value across diverse industries.
How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) being used with Augmented Reality technology?
AI is playing a crucial role in advancing augmented reality technology by unlocking a new category of use cases. AI enhances AR systems' capabilities to recognize objects more accurately and efficiently.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used to train augmented reality apps to improve object recognition and contextual understanding.
Additionally, AR devices leverage LLMs to better interpret the real world, collect data, and generate valuable insights. This is achieved through the integration of multiple sensors, enabling multimodal LLMs to process diverse inputs and create richer, more immersive experiences.


